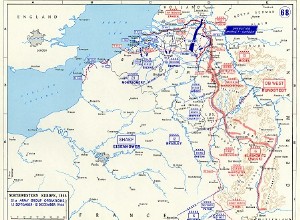
1944 August 25-27 :the 12th and 30th British corps cross the SeineAugust 29 :the 30th corps begins its march on Belgium, but the opposition of the Germans limits its advance to 30 kilometers.August 30 :the 30th corps is ordered to seize the bridges near Amiens.August 31 :at 11 oclock, all the bridg