TheWorld War I (1914-1918) was the result of permanent friction caused by imperialism between the great European powers.
The conflict lasted four years and began on July 28, 1914 and ended on November 11, 1918, with the victory of the Triple Entente formed by France, England and the United States.
The Great War, as it was called before the Second World War, was a conflict on a global scale. It started in Europe, involved the colonial territories of Africa and Asia and countries of America.
Two blocks faced each other:the Triple Alliance , formed by Germany, Austria and Italy, and the Triple Entente formed by France, England and Russia.
The contest involved 17 countries from five continents such as:Germany, Brazil, Austria-Hungary, United States, France, British Empire, Turkish-Ottoman Empire, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Kingdom of Romania, Kingdom of Serbia, Russia, Australia and China.
The war left 10 million soldiers dead and another 21 million wounded. Also 13 million civilians lost their lives.
Read Triple Alliance
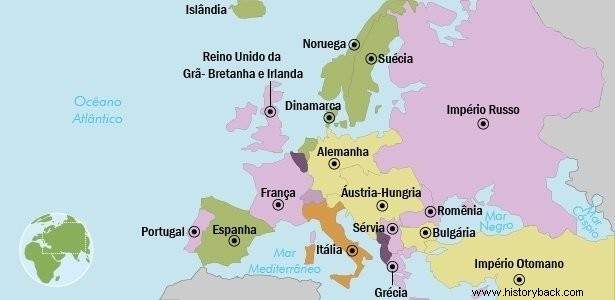
Causes of the First World War
Several factors triggered the First World War.
Since the end of the 19th century, the world has been in tension. The extraordinary industrial growth made possible the Arms Race, that is:the production of weapons in an amount never imagined.
The expansionism of the German Empire and its transformation into the biggest industrial power in Europe gave rise to enormous distrust between Germany and France, England and Russia.
Background of the First World War
We add the old rivalries between France and Germany, Russia and Germany, and the UK and Germany. Also the disagreements about the boundary issues in the colonies generated by the Berlin Conference (1880).
French anti-Germanism developed as a consequence of the Franco-Prussian War. The defeated France was forced to hand over to the Germans the regions of Alsace and Lorraine, the latter rich in iron ore.
The Russo-German rivalry was caused by the German intention to build a railway linking Berlin to Baghdad, which passed through oil-rich regions where the Russians wanted to increase their influence.
English anti-Germanism is explained by German industrial competition. On the eve of the war, German products began to arrive in markets that were dominated by England.
All these issues made conflict inevitable as clashes of economic and political interests between the industrialized powers intensified.
Read more at What is Nationalism?
World War I fuse
The alliance network was a bomb ready to explode.
In 1908, Austria announced the annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, against Serbian and Russian interests.
In order to show a good relationship between the new subjects, the heir to the Austrian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, paid a visit to the region together with his wife on June 28, 1914. On this day, a Bosnian student murdered Franz Ferdinand and his wife in Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia.
This double murder was the pretext for the outbreak of the First World War that lasted until November 11, 1918.
Read more at Causes of World War I

Phases of the First World War
At the beginning of the conflict, the forces were balanced, in number of soldiers, but they differed in equipment and resources.
The Triple Entente, for example, did not have a long-range cannon, but dominated the seas, thanks to British power.
War tanks, battleships, submarines, large-caliber howitzers and aviation, among other technological innovations of the time, constituted warlike artifacts of great destructive power.
With heavy artillery and 78 divisions, the Germans passed through Belgium, violating the neutrality of this country. They beat the French at the border and headed for Paris.
The French government was transferred to Bordeaux and in the Battle of the Marne, it contained the Germans, who retreated.
Afterwards, French and Germans established positions by digging trenches along the entire western front. Protected by barbed wire, armies buried themselves in the holes, where mud, cold, rats and typhus killed as much as machine guns and cannons. This moment of conflict is called Trench Warfare.
In 1917, the United States, that had kept out of the war, despite lending capital and selling weapons to the Entente countries, mainly to England, they declared war on Germany.
That same year, Russia left the conflict, due to the Revolution of 1917, which overthrew the tsar and implanted the socialist regime.
Consequences of the First World War
Although Germany continued to suffer successive defeats and its allies had surrendered, the German government remained at war. Hungry and tired, the German people revolted and the soldiers and workers forced the kaiser (emperor) to abdicate.
A provisional government was formed and the Weimar Republic was proclaimed. On November 11, 1918, the new government signed the German surrender. The First War was coming to an end, but general peace was only signed in 1919, with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles.
Among the terms of the treaty was the cession of regions of German territory to bordering nations.
Germany also lost its African colonies and the Weimar Republic was forced to accept independence from Austria. Likewise, it had to pay a compensation of 33 million dollars for the damages caused by the conflict.
The terms were considered demeaning and were used to bring about the fall of the Weimar Republic in 1933, and the subsequent consolidation in power of Adolf Hitler and Nazism. Thus, in 1939, just over 20 years later, they provoked the Second World War.
Reactions to the effects of the treaty are among the main consequences of the First World War.
The Great War left profound consequences for the entire world. We can highlight:
- redrawn the political map of Europe and the Middle East;
- marked the downfall of liberal capitalism;
- motivated the creation of the League of Nations;
- allowed the economic and political rise of the United States.
Brazil in World War I
In April 1917, the Germans sank the Brazilian merchant ship Paraná in the English Channel. In retaliation, Brazil breaks off relations with the aggressors.
In October, another Brazilian ship, the Macau, is attacked. At the end of 1917, a medical team and soldiers arrived in Europe to help the Entente.
Read Brazil in World War I
World War I - All MatterVestibular Questions
1. (Acafe-2015) The beginning of the First War (1914/1918) completed its centenary in 2014. Conflict of great proportions, it was the result of economic, imperialist and nationalist disputes in an industrialized Europe.
Regarding the First World War and its context, all alternatives are correct, except for:
a) The Balkan question highlights the disputes between Germany and Hungary for the control of the Adriatic Sea and puts in shock the nationalist movements:pan-Slavism, led by Serbia and pan-Germanism, led by the Germans.
b) Despite having started the war as an ally of the Triple Alliance, Italy joined the Triple Entente for having received a proposal for territorial compensation.
c) Russia did not remain in the war until it ended. Because of the Socialist Revolution, a treaty was signed with the Germans and the Russians withdrew from the war.
d) When the war started, crowds took to the streets in the countries involved to celebrate the conflict:loyalty and patriotism were watchwords.
Letter A:The Balkan question highlights the disputes between Germany and Hungary for the control of the Adriatic Sea and puts in shock the nationalist movements:pan-Slavism, led by Serbia and pan-Germanism, led by the Germans.
2. (FGV-RJ 2015) Regarding the Brazilian participation in the First World War, it is correct to say:
a) The Brazilian government declared war on Germany, in 1914, after the torpedoing of a ship, loaded with coffee, which had just left the port of Santos.
b) The Brazilian government remained neutral throughout the conflict due to the interests of the Minister of Foreign Affairs Lauro Muller, of German origin.
c) From 1916, the Brazilian Army participated in battles in Belgium and northern France with thousands of soldiers landed in the region.
d) Brazil sent a medical mission, a small contingent of Army officers and a naval squadron, which was involved in some confrontations with German submarines.
e) Together with Argentina, the Brazilian government organized an international naval squadron tasked with patrolling the South Atlantic against German offensives.
Letter D:Brazil sent a medical mission, a small contingent of army officers and a naval squadron, which was involved in some confrontations with German submarines.
Read more:
- Phases of the First World War
- Main Battles of World War I
- Questions about the First World War
