He lived at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, when modernity was being born. He epitomized progress, and many of his brilliant ideas underpin the technologies indispensable today. He was - as it was said directly - "the ruler of thunder." But not only!
1. Alternating current
One of Tesla's greatest achievements was finding a practical application for alternating current.
The inventor constructed a multi-phase electric motor that uses the properties of this current to create the effect of a rotating magnetic field, which causes the device to rotate. Such a drive was more effective than the DC motors used so far, it was also characterized by a much lower failure rate.

Nikola Tesla on a Serbian 100 dinar banknote.
The alternating current itself made it possible to transmit energy over long distances, due to the ability to easily raise the voltage with transformers, which translated into lower losses resulting from the resistance of electrical cables.
However, the public was not immediately convinced of the system proposed by Tesla. One of his main opponents was Thomas Alva Edison - his former employer and rival, basing his technical solutions on direct current (read more about Edison and his scams in our other article) . The most important argument drawn by the opponents was the greater threat to life in AC electrocution.
Both systems were used in parallel in the interwar period. Ultimately, however, this solution proposed by Tesla won. Today, alternating current is found in all electrical sockets in our homes.
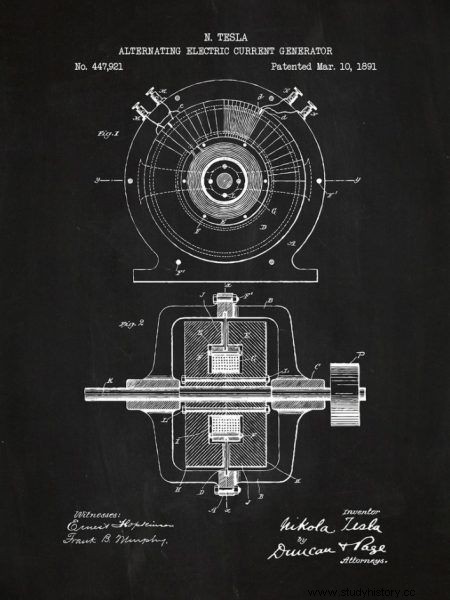
AC generator, 1891. The most famous patent by Nikola Tesla.
2. Resonant transformer
Nikola Tesla is sometimes called "the lord of lightning" for a reason. The Serbian inventor owes this nickname to one of his greatest inventions - the resonant transformer presented in 1891, also commonly known as the Tesla coil.
It is a type of air transformer in which both windings operate at the same high resonant frequency. This allows for very high electrical voltages, measured even in millions of volts. As a result, the device can generate extremely spectacular electrical discharges.
Tesla used this invention in his public presentations and readings to the delight of the public.
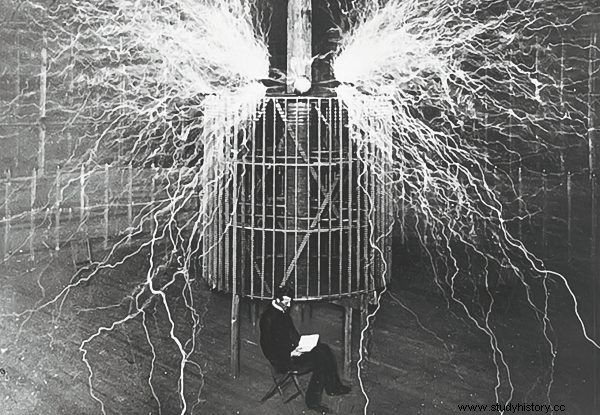

Nikola Tesla against the backdrop of his famous invention.
The spectacular nature of the device made the creators of popular culture quickly become interested in it. It was used in early science fiction and horror movies to create the lightning effect. Tesla coils were also used by stage artists, delighting the audience with the trick of touching the discharges generated by the device - high-frequency alternating current does not usually cause an electric shock effect, but it can cause painful burns. Their profession, however, was associated with a lethal risk, as failure of the device during the show could lead to fatal shock.
Currently, Tesla coils are a frequent topic of projects by amateur electronics enthusiasts. With the advent of the semiconductor era, they also gained another "entertainment" function - alternating current in the coil circuit can be modulated by acoustic frequency, so that the sounds generated by the discharge can make music.
3. Wireless electricity transfer
The resonance transformer generates not only impressive electromagnetic discharges, but also a strong, alternating electromagnetic field. Nikola Tesla in the course of his experiments with great success used them to transmit electricity over short distances. He delighted the audience by lighting light bulbs not connected to the mains, and glass tubes filled with rare rare gases glowed near the transformer.
The inventor did not manage to fulfill his greatest dream of wireless energy transmission over long distances, but it should be noted that the described experiments constitute the cornerstone of many solutions that we use every day.

Nikola Tesla on the cover of Time magazine and a dedicated article on the front page of the New York Times.
Popular wireless chargers used in modern cell phones use a variable electromagnetic field to transmit energy. In this way, the electronics installed inside the RFID proximity cards, used e.g. when authorizing electronic transactions.
4. Radio engineering and remote control
While it is not possible to identify a specific person who is the "inventor of the radio", there is no doubt that Nikola Tesla contributed a lot to the development of young radio technology through experiments on the technique of fast-changing currents.
In 1898, he obtained a patent for a remote-controlled boat model. In the same year, the inventor delighted the audience gathered in Madison Square Garden in New York, presenting the prototype of the device. The boat was swimming in a small pool, twisting, accelerating and slowing down at the inventor's will, expressed by the movements of the levers on the transmitter panel. Some visitors reacted with disbelief, considering the presentation as a clever illusionist trick - the general public was not yet aware of the experiments with the new invention, which was the radio.
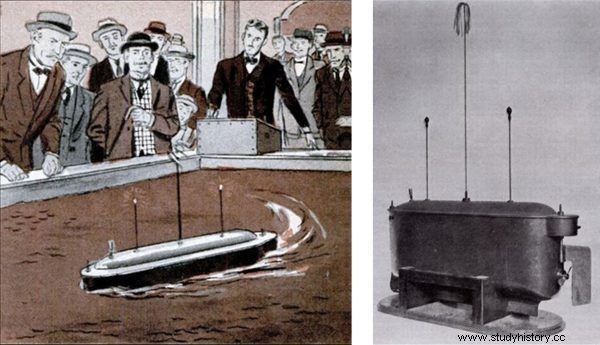
Nikola Tesla's RC Boat and its presentation in New York.
Tesla's presentation opened up new possibilities for the field of engineering known as telemetry and dealing with the remote control of devices. Until now, wired connections have been used for this purpose, which severely limited the usefulness of such solutions. Obviously, the military quickly became interested in the invention, seeing it as having a considerable military potential - experiments on remotely controlled torpedoes and airplanes began.
One hundred years later this process resulted in the creation of remotely controlled drones, commonly used by all major armies in the world.
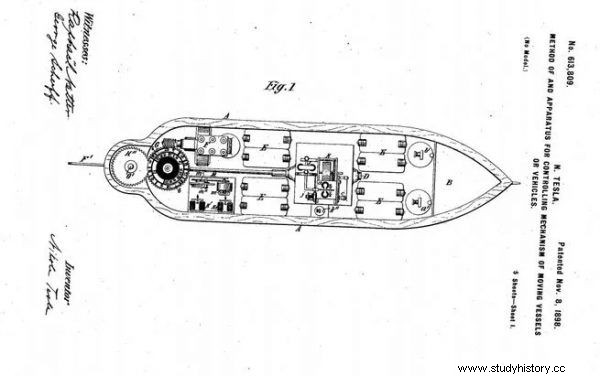
Tesla's patent for a RC boat.
A working replica of the aforementioned boat model can now be seen at the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade.
5. X rays
Few people are aware that Nikola Tesla was one of the pioneers of X-ray science. Experimenting with Crookes tubes (a type of glass bulb with two embedded electrodes and air pumped out of it) connected to a high-voltage source, he observed the emission of penetrating radiation, invisible to the human eye.
These experiments were performed independently of similar attempts by the German physicist Wilhelm Xentgen, widely recognized as the discoverer of X-rays, a type of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.

Nikola Tesla was also one of the discoverers of X-rays.
In the following years, after the publication of X-ray's work, Tesla continued to work in this field, becoming one of the pioneers of X-ray photography.
6. Disc turbine
In 1913, Tesla patented a bladeless disc turbine - it was the hundredth American patent obtained by a scientist. The device consisted of a set of metal targets placed at short distances from each other. These discs were set in motion by a pressurized liquid moving in the spaces between them.
Tesla's patent list also includes numerous improvements to existing devices. The inventor dealt mainly with the subject of electricity. He experimented with various methods of its production and distribution, and worked on improvements to existing electric motors and light sources. At the same time, he did not shy away from other challenges - later in his life, he became interested in, for example, aviation technology, even obtaining a patent for a type of aircraft, equipped with a set of movable propellers, designed to enable vertical take-off and landing.
Bibliography:
- Cheney Margaret, Uth Robert, Tesla:Master of Lightning , New York 1999.
- US Patent 433702 A, Electrical transformer or induction device . Google Patents.
- US Patent 1061206 A, Turbine, Google Patents.
- US Patent 1655113 A, Method of aerial transportation . Google Patents.
- US Patent 1655114, Apparatus for aerial transportation, Google Patents.
- Wróblewski Andrzej Kajetan, History of Physics. From the earliest times to the present day , PWN, Warsaw 2009.
Find out where to buy "Last Days of Darkness":
