The World War II , which took place between 1939 and 1945, left thousands dead, countless injured and redefined the world's balance of power.
The main consequences of this conflict were the rise of the United States, the division of the world between capitalism and socialism and the emergence of the UN.
In Brazil, there is the end of the Getúlio Vargas government and the rapprochement with the Americans.
Number of Victims of the Second World War
The conflict, according to some estimates, killed 45 million people and injured 35 million. The highest number of casualties was recorded in the Soviet Union with 20 million dead.
In Poland, an estimated 6 million casualties, while Germany accounts for 5.5 million. As a result of the conflict, 1.5 million Japanese died.
Furthermore, the Second World War produced one of the most atrocious crimes against humanity:the murder of 6 million Jews on an industrial scale.
The physical elimination of these people was part of a project by Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), known as the Final Solution. To accomplish this, the Nazis devised a complex system of extermination in concentration and death camps.
See also:Nazi Concentration CampsEconomic Consequences of World War II
In addition to human losses, the conflict cost 1 trillion and 385 billion dollars in monetary losses. Of the amount, 21% went to the United States, 13% to the Soviet Union and 4% to Japan.
All 72 countries involved accumulated losses in different proportions. There was an intense drop in industrial production and government investments were directed towards the war, to the detriment of other areas, generating intense social problems.
If for most countries there was a loss, for the United States the war resulted in the strengthening of its imperialist and economic position. After all, this country was not attacked and, therefore, it was not necessary to allocate resources for its reconstruction.
See also:North American imperialismGeopolitical Consequences of World War II
After the Second World War, new countries emerged and some had their borders redrawn.
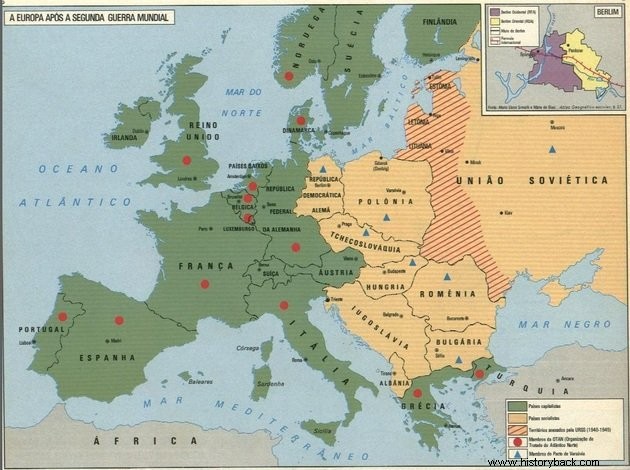
Austria, which was annexed by Germany in 1938, re-emerges as an independent country.
Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania and Yugoslavia depose the monarchy and replace it with the republican regime.
Portugal and Spain isolated themselves from the international system until the mid-1950s, due to the dictatorships of Salazar and Franco, respectively.
Countries liberated by the Soviet Union such as Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia pass into the Soviet sphere of influence; while the other countries continue with social democracy.
See also:Beginning of World War IIGermany
After the war, Germany had to accept the four "Ds" imposed by the allied powers:"denazification", demilitarization, democratization, disarmament.
Thus, some Nazi leaders were tried by the Nuremberg Tribunal. Of these, 12 were sentenced to death.
On the other hand, the country was divided into two clear areas of influence:the German Democratic Republic (GDR), with a socialist regime, and the Federal Republic of Germany (RFA), which continued to be capitalist.
In the city of Berlin, then capital of the GDR, the Berlin Wall was built, which became the symbol of the ideological division of the world.
Likewise, the Armed Forces were reduced and the country ceded facilities to accommodate both American and Soviet troops.
See also:WWIIJapan
Japan was forced to recognize the independence of Korea, return the Kuril Islands to the Soviet Union and reduce its Armed Forces.
The country had the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki destroyed by two atomic bombs dropped by the US and received 2.5 billion for their reconstruction.
See also:Causes of World War IICold War
During the conflict, the US invested approximately US$ 300 billion, which was recovered with a 75% increase in the arms industry.
The United States also became the creditor of the destroyed countries and in 1948 created the Marshall Plan. This consisted of a financial aid of US$ 38 billion to recover European industries and cities.
The US aid, however, was refused by the Soviet Union, starting the process that became known as the Cold War.
The Soviet Union extended its influence to Eastern European countries and would continue to support movements that wanted to implement socialism as a government regime.
See also:Cold War:features, causes and consequencesConsequences of World War II in Brazil

In Brazil, the Second World War directly influenced the end of the Vargas government. Intellectuals, politicians of various tendencies, and part of the population question the contradiction of sending soldiers to defend democracy while Brazil was under a dictatorship.
Getúlio Vargas is deposed in 1945 through an articulated coup between the Armed Forces and conservatives. The presidential elections take place the following year and Eurico Gaspar Dutra wins.
In turn, the Brazilian Expeditionary Force is demobilized while still in Europe, as Vargas feared that this contingent would turn against him.
Likewise, Brazil remains politically and culturally aligned with the United States, whose approximation was due to the Good Neighbor policy.
However, for its participation in the conflict, Brazil is invited to join the United Nations (UN).
Want to know more? Read here:
- UN (United Nations)
- Questions about the Second World War
- Manhattan Project
- Brazil in World War II
- Films about the Second World War
- 6 Films About Hitler, the Dictator of Nazism
