The Romanesque Art refers to a style that emerged during the Middle Ages, more precisely in the High Middle Ages (between the 11th and 13th centuries).
The term “Romanesque ” is closely related to the influences of the Roman Empire, which for centuries dominated almost all of Western Europe.
Characteristics of Romanesque Art
The Romanesque style stood out in architecture, painting and sculpture. Although it has had greater relevance in the architecture of religious buildings.
Romanesque Architecture
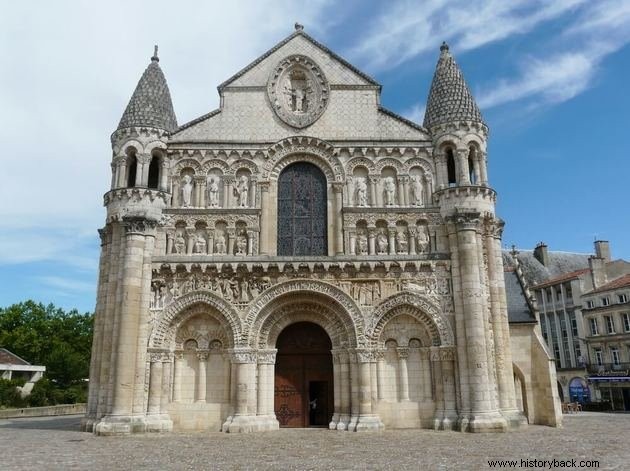

In Romanesque architecture, we can highlight some characteristic elements, such as the horizontality, that is, the buildings did not have very tall structures. Several churches, monasteries, convents and cathedrals were built in this style.
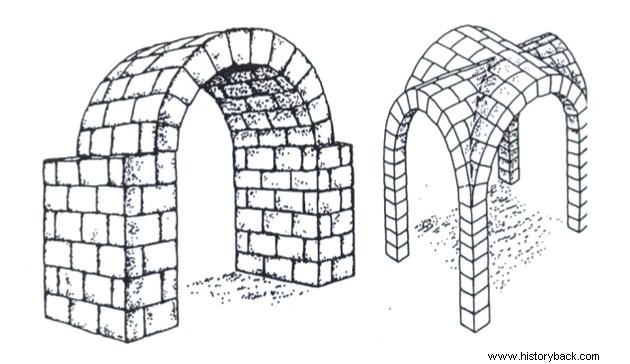
There was also the use of vaults , which could be of two styles:cradle and edge ones.
The barrel vaults were more simplified, based on a semicircle structure called a full arch. Due to some disadvantages in this type of construction, such as low light and risks of collapse, a new style was created, the edge vault.
In it, two barrel vaults were supported on pillars, at right angles. In this way, they were able to create better lit and safer environments.
We can also point out other particularities, such as the thick walls and a sparsely decorated interior. In addition, the plans of Romanesque buildings were shaped like a cross and were solid buildings made of stone.
They still had few windows and openings and usually had a main door, the entrance.
Because of their grandeur and solidity, they were called "Fortresses of God".
See also:Medieval ArchitectureRomanesque Painting

Biblical and religious themes mark Romanesque painting. Usually, these paintings adorned the churches and cathedrals of the time.
The fresco technique was used, in which the painting was done on a damp wall. Miscellaneousmurals , illuminations and tapestries appear with religious themes. Made in bright and strong colors, they filled the walls of religious temples.
That's because in the Middle Ages, few knew how to read and write and, thus, these paintings served as “religious literacy” for the most lay people.
As main characteristics of the painting of this period, we have deformation and colorism, namely:
- Deformation:to convey religious sentiments, figures were not always produced in the right proportions. Thus, Jesus could be portrayed larger than the other characters to bring out the notion of magnitude.
- Colorism:application of pure colors, without halftones and concern for light and shadow games.
Romanesque Sculpture
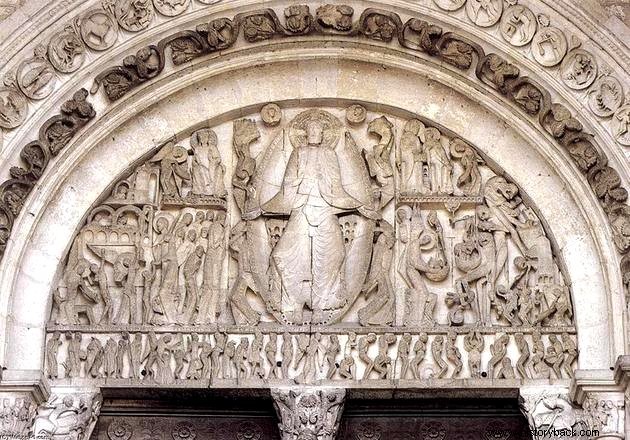

As in Romanesque painting, Romanesque sculptures were produced to adorn sacred sites.
Therefore, the major theme revolved around religiosity, since in that period theocentrism (God as the center of the world) was a strong characteristic.
They were anti-naturalistic sculptures and usually represented by figures carved into the walls of churches. Some reliefs also adorned the facades.
In the last phase of Romanesque art it is possible to find a more realistic style in the sculptures.
See also:Medieval ArtRomanesque and Gothic Art
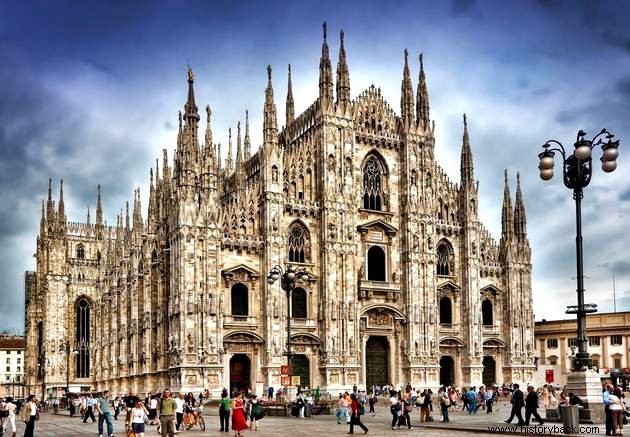
During the Middle Ages, two styles prevailed:the Romanesque style and the Gothic style. After the Romanesque, the Gothic style appears in the Late Middle Ages.
In Gothic architecture, the style was marked by the verticality and monumentality of its constructions.
In addition, another important characteristic of Gothic art is related to the use of stained glass in its constructions.
 See also:Gothic Art
See also:Gothic Art Fun facts about Romanesque Art
Many Romanesque buildings were intended to house pilgrims, so they were erected on the paths of sacred sites. This is why the churches of this period became known as Pilgrimage Churches .
Currently, it is possible to find in Europe several buildings in Romanesque style. In Portugal, there is a tourist-cultural route called Romanesque Route . It is made up of 58 monuments and buildings designed in the Romanesque style.
See also:What is Sacred Art?