Leonardo da Vinci was one of the most important Italian artists of the Renaissance period.
Renaissance scholars recognize him as perhaps the most significant figure of his time.
It was what you might call a genius , dedicating himself to studies in various fields of art and knowledge at a time when intense transformations took place that guided the world towards modernity.
It was in painting that Da Vinci found his greatest prominence. About painters, he once said:
Da Vinci Biography
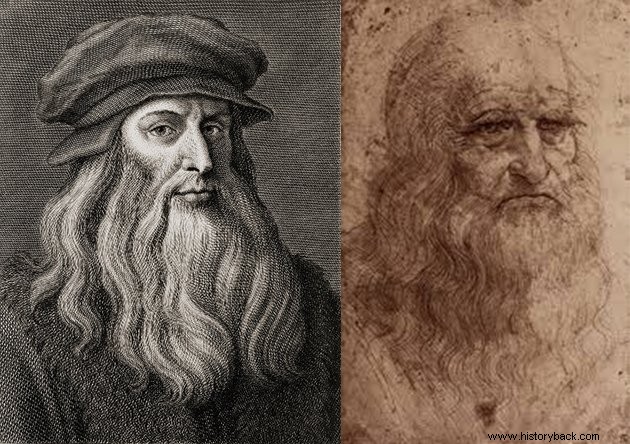

Leonardo da Vinci was born in Anchiano, a small Tuscan village near Vinci and near Florence, Italy, on April 15, 1452.
At the age of 17 he studied Arts in the studio of master Andrea del Verrocchio, where he modeled images in terracotta. He worked for important figures such as Lorenzo de Medici, governor of Florence.
In 1480 he painted the canvas Virgin of the Carnation , considered his first solo work.
Between 1482 and 1499 he lived in Milan, where he was a protege of Ludovico Aforzo, Duke of Milan, for whom he painted the fresco “The Last Supper ” to the Monastery of Santa Maria delle Grazie. He also provided services to the Duke as an architect and engineer, as well as a painter. The work Vitruvian Man. dates from this period.
In 1503 he realized what would become his great work, Mona Lisa , using the sfumato technique . In this method, the artist produces smooth gradients in the tones, which makes it possible to represent the texture of human skin. Leonardo da Vinci was a great fan of this way of painting and used it a lot in his paintings.
Still at that time, he served as a strategist for César Borgia, an Italian cardinal and nobleman. From 1503 to 1516 he lived in the Vatican, period of great activity of Raphael and Michelangelo - other important artists of the period. At the behest of Pope Leo X, he carried out a series of brilliant studies of optics.
During the occupation of Italy by the French, da Vinci designed a residence for Governor Carlos d'Amboise whose boldness earned him an invitation from French King Francis I to live in France, where he carried out work at the court.
He died at the age of 67 on the 2nd of May 1519 in France and was buried in the palace of Amboise.
See also:Renaissance:Characteristics and Historical ContextLeonardo Da Vinci's Major Artworks
Leonardo da Vinci painted few paintings, however, all of them are true masterpieces.
Da Vinci's work was based on the realism of figures and valued the value of lights, shadows and reliefs. About this, the artist explained.

The works deserve to be highlighted:
- "Announcement ", exhibited at the Galleria Degli Uffizi, Florence, Italy;
- "Mona Lisa ", considered the best-known painting in the world, exhibited at the Louvre Museum in Paris, France;
- "Vitruvian Man ", an engraving exhibited at the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice, Italy;
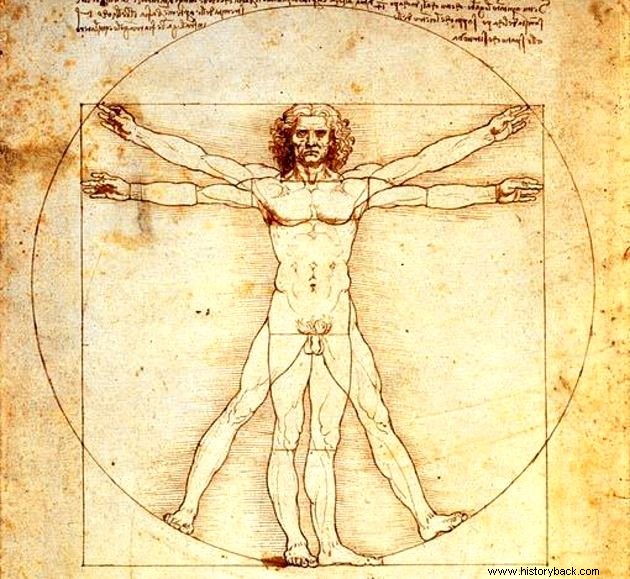
There are also important works by the artist:
- "Virgin of the Rocks ", one of them exhibited at the Louvre Museum, Paris; and another, at the National Gallery, London;
- "The Last Supper ", fresco located in the Church and Convent Santa Maria Delle Grazie, in Milan, Italy;
 See also:Art Revival
See also:Art Revival Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions
Leonardo da Vinci was a multifaceted figure who excelled in the arts and sciences. He is considered a polymath , that is, a wise person who has in-depth knowledge of several areas.
Thus, Leonardo was a painter, sculptor, mathematician, architect, urban planner, physicist, astronomer, engineer, naturalist, chemist, geologist, cartographer, strategist, creator of war devices and inventor of musical instruments.
In all of his creations, Leonardo discussed any established truth. Before accepting an idea, he made a point of testing it in various ways to draw his conclusions. His empiricism was later imitated by the physicist Galileo Galilei and the philosopher Francis Bacon.
- Arts – In addition to painting, where he distinguished himself most, Leonardo dedicated himself to sculpture, where he made sketches, but few works he completed.
- Urbanism – until the Renaissance, cities were nothing more than unhealthy clusters of houses, with few streets and no sewage. In the project he did for the city of Milan, da Vinci drew sewer channels, banished walls, designed squares and gardens. He predicted large, ventilated houses and pedestrian streets and free lanes for vehicles.
- Hydraulic – based on Archimedes' principle, Leonardo invented a hydraulic pump to raise water, thus creating the first of lifting devices. He also imagined a well pump and a water wheel, paving the way for turbines, which the world came to know only later.
- Engineering – in addition to being an aeronautical and hydraulic engineer, Leonardo was also a civil engineer. He predicted the technique of building metal bridges.
- Anatomy – Because of anatomy, he was almost arrested for being caught dissecting corpses, which was considered a serious crime. He made important discoveries, which he recorded in numerous drawings and in the "Treatise of Anatomy "which he wrote.
Mastery of the air has always been one of Leonardo da Vinci's passions. After studying birds in depth, in search of knowledge about flight, he conceived a device very similar to them.
He came to the conclusion that the man would never fly, but he could safely land with the gliders.
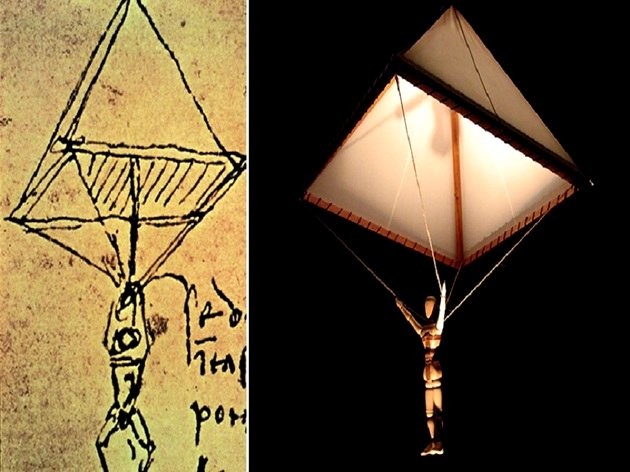
He created a parachute and several other aerial machines. Despite being fascinated by life, he also created very efficient defensive systems for those who hired him as a strategist.
See also:Cultural RenaissanceFun facts about Leonardo da Vinci
We selected some curiosities about this important personality. See!
- The artist was the illegitimate son of Piero da Vinci and was raised by his grandparents.
- Leonardo da Vinci was left-handed. It is said that he could write with his left hand while drawing with his right.
- He was also in the habit of writing backwards, from left to right.
- Da Vinci never attended a university and his training was with Andrea del Verrocchio;
- Leonardo da Vinci did not eat meat and used to buy caged birds to release them in the wild.
- The first bicycle project was done by Leonardo.
To also know other works and artists of the period, read :
- Artists of the Renaissance
- The Creation of Adam:Analysis of Michelangelo's Work
- Sandro Botticelli
