The “War of Secession” or “American Civil War” was a civil war that took place in the United States of America between 1861 and 1865.
The conflict involved the Northern States (Union) and the Southern States (Confederate States of America) for the emancipation of slaves and ended with the victory of the Union.
This was the first modern warfare where repeating rifles, trenches, battleships and submarines were employed, as well as aerial reconnaissance balloons.
After the conflict, the main difference between the northern and southern states - slavery - disappeared, making it possible for them to unite. However, racial segregation also began at this time leaving thousands of African Americans without the same rights as whites.
Causes of the Civil War
Slavery
The main cause of the conflict is linked to the slavery issue, as the North defended the abolition of slavery and the South was against such measure.
Differentiated colonization
Since colonial times, however, North and South have had a distinct socio-economic development, marked by geographic differences between the Thirteen British Colonies.
The established colonies in the North had a cold climate similar to that of England. In this way, the settlers reproduced there the same activities that they carried out in their place of origin, such as subsistence agriculture, commerce and manufacture.
On the other hand, in the South, the warm climate favored agriculture under the Plantation system. This consisted of large monoculture properties, slave labor and foreign market, favoring a rural and aristocratic lifestyle.
Different economic policy
While the North region was increasingly industrialized, the South became agricultural. Inevitably, this led to the collision of interests of the two regions during the independence process.
The North wanted a protectionist and abolitionist economic policy. For their part, slaveholders and Confederate aristocrats preferred to maintain slavery.
The South, then, secedes from the Union, proclaiming itself the Confederate States of America, in 1860. The North of the country did not accept this decision, deeming it unconstitutional and war was declared in the same year. Likewise, no foreign country has recognized it as an independent nation.
Features of the Civil War
The Union armies, under the command of General Ulysses Grant, had well-equipped soldiers in greater numbers, because the North region was more industrialized and populated.
However, the southerners, commanded by General Robert Lee, had a military tradition and experienced commanders, which made them a difficult adversary to defeat.
Both the Union and the Confederacy started the war using volunteers, but soon adopted the forced recruitment of the population.
Confederate troops were poorly paid and poorly equipped. They were usually armed with a single-shot rifle, clothes made of raw wool, and normally wore no shoes.
In the North, where about 22 million people lived, it was possible to recruit more than two million soldiers, 180 thousand African Americans. Of these, approximately 1.12 million were part of the Union army at the end of the conflict.
Nevertheless, the Confederacy, with just under 10 million inhabitants, managed to recruit more than a million soldiers and only 500,000 remained until the end of the war.
As for the Navy, we can say that the Union was hegemonic from start to finish, as it had 56,000 sailors and 626 ships, 65 of which were battleships. On the other hand, Confederate naval forces were smaller, reliant on the purchase of European ships and the capture of Union ships.
Historical context and development of the war
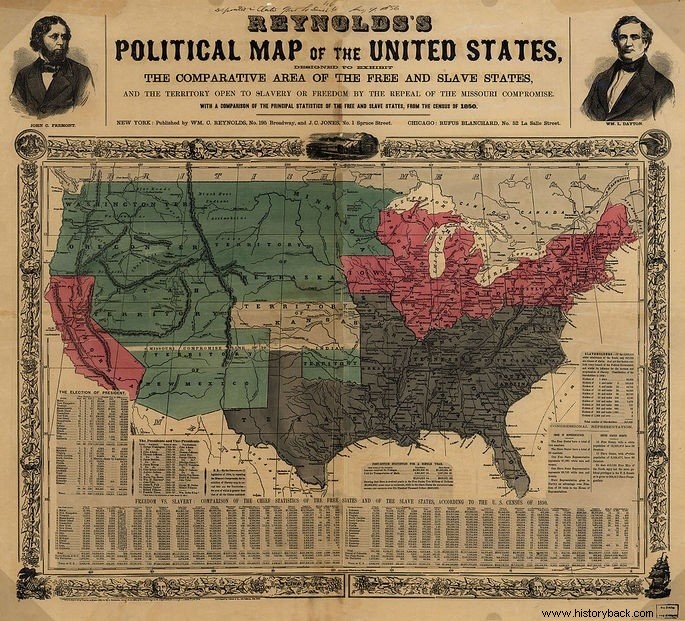
Since 1850 it was possible to perceive the hostility between the North and the South over the slave issue.
There was an attempt to resolve it through the "Compromise of 1850" which made an exception for free labor in California, although the state was in the South.
As early as 1854, the Kansas-Nebraska Act authorizes slave labor in these states even though they were in the north. Two years later, the people of Kansas voted against slavery, however, the Southern-dominated Senate did not accept the popular decision.
Thus, in the year 1858, the Democratic Party splits between pro-abolitionists in the North and pro-slavery in the South, where the abolitionist John Brown is sentenced to death for inciting a rebellion in 1859.
In 1860, the Northerners dominate the Senate and, led by the Republican Abraham Lincoln, begin to fight slavery in the United States. Lincoln wins the 1860 presidential election, triggering a hostile reaction from the South.
In the same year, South Carolina withdraws from the Union, followed by Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana and Mississippi. At the start of the fighting, Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia and Texas also withdrew from the Union.
Then, in December 1860, a new country appears, the Confederate States of America, whose president-elect was Jefferson Davis of Mississippi and the capital, Richmond, Virginia. The Union does not accept the separation, alleging the unconstitutional act and declares war on the Confederates.
Also called unionists, the Union consisted of the states of California, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon , Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont and Wisconsin, Colorado, Dakota, Nebraska, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Kansas and Washington,
Main facts of the Civil War
Hostilities began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked and captured Fort Sumter. In response, the Union prepares for war.
Starting in 1862, executing the “Anaconda Plan”, the Union imposed a siege on the Confederation by land and by sea, blocking all exports of cotton, tobacco and food, as well as the importation of war material.
In that same year, the Confederate troops suffer from the defeat at Antietam and bitter the destruction of their navy on the western front. In 1863, despite the efforts of General Lee, who defeated Union forces in Virginia, the Confederate incursion into the North ends with the Southern defeat at the Battle of Gettysburg.
Realizing the impending defeat of the South, the United Kingdom declares itself neutral and withdraws from the conflict. Meanwhile, on the western front, Union troops destroy all Confederate infrastructure to the east, until they capture Richmond, capital of the Confederate States of America, on April 10, 1865.
However, on April 14, 1865, Lincoln is assassinated by a southerner. At the end of this year (1865) the 13th Constitutional Amendment was passed, abolishing slavery in the USA.
End of the Civil War
Defeated on the battlefield, on June 28, 1865, the Confederate generals surrender, beginning a period of reconstruction that lasted until 1877, when Union troops left the South.
It is estimated that military casualties exceed 600,000 dead and 400,000 wounded, between both sides. The majority of these casualties (about three-fifths) were caused by illnesses contracted due to poor food and medical hygiene.
Furthermore, in 1868, the 14th Constitutional Amendment was enacted, which obliges all US states to comply equally with the Constitution.
Consequences of the Civil War
Without the amount of industries that the North had, the defeat of the South was inevitable and was followed by a strong political-economic recession. Southern fields and cities were destroyed by Northern armies and states lost their political influence in the United States.
Despite the end of slavery, the black population would live in segregation for a long time. In some southern states, racist organizations such as the Ku Klux Klan were created to combat the integration of African Americans into American society.
On the other hand, the North region benefited from the Civil War, as there was a great expansion of the industrial sector. After the war, the western territories were incorporated into the new unified state and made possible the construction of railways, telegraph lines and cities.
As the Union won the war, the industrialist model of the North became hegemonic in the United States and guided the country's economic development.
