Central America it is an isthmus that joins South America and North America. It is limited to the north by the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico and to the south by Colombia, limited to the west by the Pacific Ocean and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean.
Central America represents a mountainous area with an extension of 523,000 km2 and is one of the regions with the highest number of active volcanoes (the continent is located on the Caribbean Tectonic Plate).
There are mountains throughout the region (most are volcanic), the highest being Mount Tajumulco, in Guatemala, with an altitude of 4,220 meters.
The longest rivers in Central America flow into the Caribbean, while the smallest flow into the Pacific. There are three large lakes:Nicaragua, Managua and Gatún.
In addition to Spanish, the official language of several countries in Central America, other languages are also spoken, such as English in Belize, Dutch and Papiamento in Aruba, French in Haiti, in addition to numerous other dialects that are spoken in Central America.
The majority of the inhabitants of Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, El Salvador and Panama are made up of mestizos (mixture of Indian and white), with a small number of whites. Most of the population is Catholic
Countries of Central America
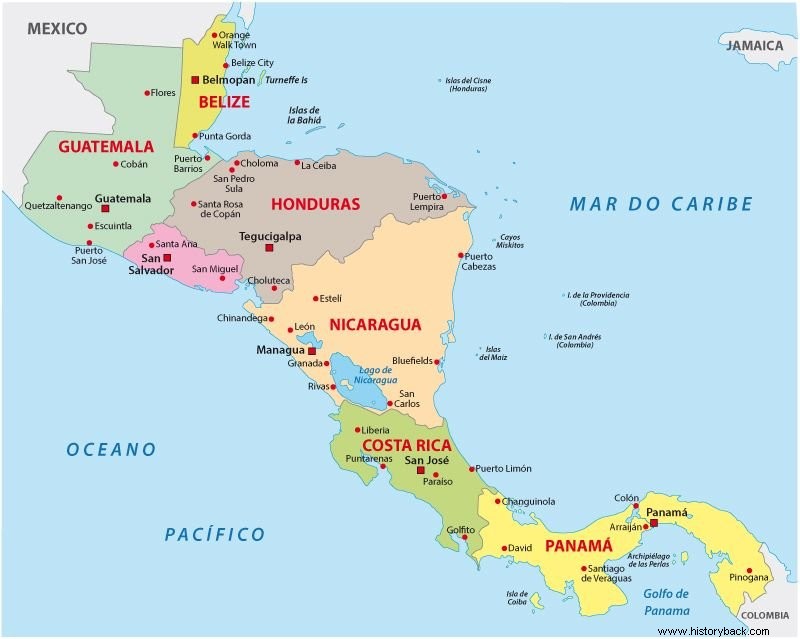 Political Map of Central America
Political Map of Central America
Central America is made up of 20 countries :
- Belize
- Costa Rica
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Grenade
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
In addition, other countries have territories in the region:the United States has Puerto Rico, Navassa Island and the US Virgin Islands; France has Saint Bartholomew and Saint Martin; the Netherlands has Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles; and the UK owns Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Monserrat, the British Virgin Islands and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
See main data for each country in:Central American Countries
Colonization and History of Central America
In the beginning, Central America was populated by several aboriginal groups, the most important being the Mayan civilization.
Subsequently, colonization will begin in the 16th century, starting from the Caribbean colonies of Hispaniola and Cuba.
The conquest of the region was, however, the task of Hernán Cortés and others, while the spiritual conquest was the work of Friar Bartolomeu de las Casas.
During the colonial period, all of Central America was included in the Captaincy General of Guatemala, thus forming part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain and falling under the jurisdiction of the Viceroy who ruled from Mexico City.
With the independence of the Isthmian Central American countries from Spain in 1821, most of the area was annexed until 1822 to the Mexican Empire of Augustín de Iturbide.
Furthermore, the British established themselves on the Atlantic coast, with trading posts, for the exploitation of pau-campeche, constituting the colony of Belize, despite the efforts made by the Spaniards to recover the region.
Economy of Central America
1. Industry
Industrial manufacturing is restricted to the processing of agricultural articles for export and the production of consumer goods and construction materials intended for domestic use, while the production of coffee, cotton and other textile fibers, leather and wood are linked to the economy. from all countries.
The transformation industry, on the other hand, is conceived by factories of food products, beverages, cigarettes, fabrics, shoes, etc. The most industrialized country in the region is El Salvador.
2. Agriculture and livestock
The lands of the humid lowlands on the Atlantic side and the Panamanian Pacific coast have a shallow fertility, with the volcanic areas of El Salvador, Nicaragua and Guatemala being the best agricultural lands in the entire region, as well as the forested regions of the highlands of Costa Rica. .
Cattle are raised, mainly in Honduras, while in other environments volcanic ash has fertilized the land allowing for the planting of bananas, sugar cane, corn and fruits.
Subsistence agriculture is the dominant activity among Central American populations, with the main articles of this agriculture being corn, beans, squash, fruits, yucca and sweet potatoes.
In terms of exports, coffee (grown in the highlands) and bananas represent four-fifths of the total revenue obtained.
The largest banana plantations stretch across the tropical lowlands of both the Atlantic and the Pacific.
Other products such as tobacco and wheat are produced in small quantities, while sugar cane is grown on a large scale in the region.
It has certain economic importance the raising of cattle and in the Atlantic slope, of sheep, in the northern and central portions, being the goats raised in higher areas.
3. Mining and extractivism
In Central America we find large deposits of oil and gas, as well as silver and gold.
Therefore, the region still produces gold and silver, as well as zinc, lead and some non-ferrous metals.
On the other hand, half of the territory is covered by forests and has extensive and varied extractive resources, such as wood (mainly mahogany, Spanish cedar and pau-campeche), gums (notably gum), resins, tannins and medicinal products.
Fauna, flora and climate of Central America
Central America's biodiversity is very rich, as there are several tropical forests with a large number of animal and plant species.
Thus, the fauna of the region is a composition of the South American (Neotropical) and North American (Neo-Arctic) faunas.
Reptiles have a complex distribution, which includes species and genera from the north and south, as well as mammals, which can count on common species throughout the American territory.
Regarding flora , we note that in the higher mountainous areas, a giant herbaceous vegetation predominates, while in the lower areas, the subtropical forest will dominate with its arboreal formations.
In the transitional regions between tropical and subtropical forests, vegetation of both types develops.
On the other hand, in the arid plateaus, squalid shrubs, xerophytic plants and cacti predominate. Palm trees will spawn in areas located below 600 meters.
Finally, the vegetation comprises dense forests that have already been deforested in almost 50% due to the exploitation of hardwood.
From weather , the categorization by altitude is notable:
- the “hot land” (regions from sea level to an altitude of 910 m);
- the “temperate land”, (regions from 915 m to 1830 m);
- the “cold land”, (regions up to 3050 m).
We can generally say that in Central America we have a hot tropical climate with a wet season in the summer and a dry season in the winter, with tropical storms being commonplace in the region.
Curiosities
- The MCCA (Central American Common Market) is the region's economic bloc for economic integration among its member countries (Nicaragua, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras and Costa Rica).
- The Panama Canal is an extensive 82 km man-made canal built from 1880 onwards in Panama.
