The Seven Years War (1756−63) was a conflict between England and France over land in North America and the Asian continent. It also involved Prussia, Austria, Portugal and Spain.
The war spread across three continents and was fought in Europe as well as America and Asia. That is why it is considered as the first world conflict.
As a consequence of this war, France loses its colonial territories, Prussia emerges as a European power and England, victorious of the conflict, becomes the most powerful country in the world.
Countries involved in the Seven Years' War
There were two main fronts of war:the first front, in Europe, between Prussia and Austria. These two nations still had not resolved their territorial differences after the War of the Austrian Succession (1740-1748) and they clashed again.
The second front of the conflict took place in America and India and is related to the colonial rivalry between Great Britain, France and Spain.
Since 1754, France and England faced each other in America for control of the Ohio Valley and, on this occasion, the French were supported by several Indian tribes, against the English.
For its part, Spain supported France, while Portugal remained neutral. The Spaniards took the opportunity to attack and occupy the Colonia del Sacramento, in South America, which at the time belonged to the Portuguese.
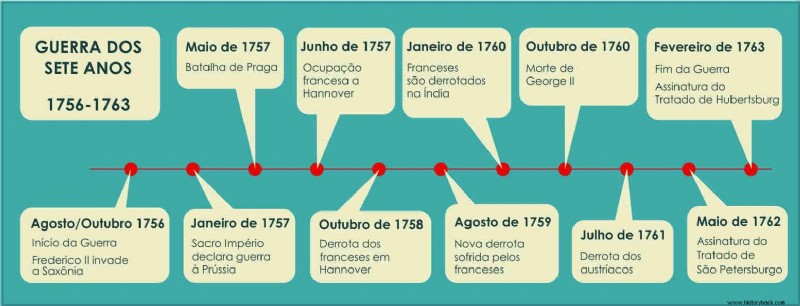 Seven Years War Timeline
Seven Years War Timeline
Causes of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War took place because of territorial disputes in both America and Europe. On the American continent, England, France and Spain fought; in Europe, these same countries, plus Austria, Prussia, the Swedish Empire, the Russian Empire and Spain.
France and England wanted to increase their possessions in America and as there were no defined borders, friction was constant. For its part, France wanted to guarantee its hegemony on the European continent, something that always made England uneasy, because a strong France meant a weak England.
The feud begins in August 1756, when King Frederick II of Prussia invades and defeats Saxony. In response, in January 1757, the Holy Roman Empire, led by Empress Maria Theresa of Habsburg, declared war on Prussia.
In the Caribbean, naval battles take place between the British Royal Navy against the Spanish and French. Meanwhile, in North America, the French lost Quebec and suffered a defeat in the Great Lakes region, to the British.
There were intense battles in the border regions between Prussia and Austria such as Silesia, Bohemia and Saxony.
Also read: The Thirteen Colonies and the Formation of the United States
End and consequences of the Seven Years' War
France was the big loser in the Seven Years' War and England the undisputed victor. In Europe, Prussia also strengthens itself as a powerful state against Austria.
Two treaties ended the conflict in 1763:the Treaty of Paris and the Treaty of Hubertusburg.
The Treaty of Paris determined the territorial organization of North and Central America between France, England and Spain:
- France cedes Canada and part of the Antilles to the British. In turn, the British return the islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe to France.
- In the Caribbean, the islands of Saint Vincent, Tobago and Dominica become British colonies, while the French keep Saint Lucia.
- The French cede the Louisiana Territory to Spain.
- Spain hands over Florida to the British and in exchange receives from them the island of Cuba.
- Spain returns Colonia del Sacramento and the island of São Gabriel, both in present-day Uruguay, to the Portuguese.
By the Treaty of Hubertusburg, Austria recognized Prussia's sovereignty over previously conquered regions.
Independence of the United States
England emerged victorious from the conflict, but faced a serious financial crisis. For this reason, it intensifies the taxes on the 13 Colonies, in order to cover the expenses generated by the battle in America.
Participation in battles and rejection of the new rates, however, strengthened the military formation and political consciousness of the colonies, which began to fight against English laws and articulate the movement that would culminate in independence in the United States.
