After World War II, during the Potsdam Conference, Germany was divided between the Allied Powers and the Soviet Union.
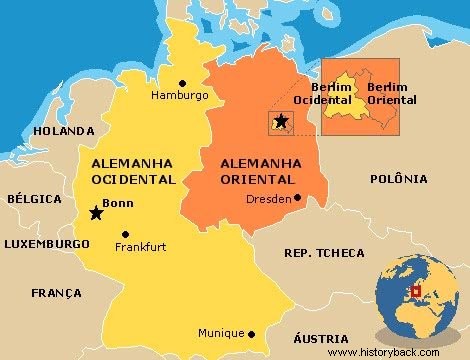
In 1949, the country was formally divided into the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) and the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany).
East Germany it was under socialist and Soviet influence, with capital in Berlin. In turn, the western part lived under a capitalist and American orbit, whose capital was Bonn.
This division followed the logic of the Cold War that dominated the world order until 1989 with the fall of the Berlin Wall.
Berlin
The former German capital did not escape this division. Berlin was located in the heart of East Germany and there, two systems of government and two currencies coexisted in the same city.
First, it was subtly divided into neighborhoods and zones destined for the capitalist side and the socialist side. However, from 1961, physically, with the construction of the Berlin Wall.
In 1953, several East German workers marched in Berlin demanding better living conditions and more freedom. They are harshly repressed by the police who shot the unarmed crowd, in addition to arresting 13,000 to 15,000 people. In the face of this coercion, around 3 million Germans pass to the West.
The more the Soviet regime dominated and repressed the population of East Germany, the more people became dissatisfied and fled to the West.
The East German authorities are looking for a solution to stop Berliners from falling to the capitalist side and building the Wall.
Read more about the Berlin Wall.
Policy
The political system in the German Democratic Republic was inspired by the Soviet socialist organization. In this way, there was a large party, the socialist and other minorities with little representation. There were no direct elections.
Opposition political parties were formally banned. The population was co-opted through social and cultural associations and groupings in order to build the new socialist man.

East German flag with hammer and square in the center.
Political Repression:Stasi
The Stasi it was the body responsible for monitoring citizens who had ideas contrary to socialism. Listening to rock music, missing the May Day rally, wearing Western clothes, questioning authority could all be viewed as suspect by the Stasi.
Artists, students, politicians, all could be targeted for investigation which also included arbitrary arrests, violent interrogations, isolation and torture.
Economy
The East German economy was based on the Soviet socialist model. Thus, the Germans adopted the model of a planned economy through the Five Year Plans. There was no private property and everything was owned and managed by the state. The war and heavy industries were privileged in this model.
Even though the basic needs of the population were covered, such as education, housing and health, there was neither political nor individual freedom. Likewise, the variety of products was minimal.
Culture
Cultural production should be designed to exalt socialist ideals and denigrate the capitalist world. Many productions were directly influenced by Soviet realism.
Works of theatre, cinema and books should have as their theme the struggle of the working class and its effort to build an egalitarian society. The artistic avant-gardes, such as abstractionism, were viewed with suspicion.
In addition, any artistic production required permission to be reproduced.
Way of Life
In order to build a society where everyone was equal, there was a generalized standardization that ranged from housing to clothing. The apartments were the same for everyone, and the variety of wallpapers, decorations and furniture was minimal.
German clothes were always standardized, except for those who could pay more. The fabrics were few and the stores sold practically the same models to the common people. The way was for women to learn to sew their own dresses and make their own accessories to differentiate themselves.
The best example of this standardization was the automobile industry. There was only one car model, the Trabant, which East Germans had to wait years and years to obtain. The model was simple and outdated, but everyone wanted to own it.

The Trabant car
End of the German Democratic Republic
In the 1980s, the Soviet model showed clear signs of economic exhaustion. Unable to keep up with the pace of capitalist industry, the industrialized products of the socialist world were outdated and had a reduced consumer market.
In 1985, Mikhail Gorbachev is elected as General Secretary of the Communist Party in the USSR and promises political and economic opening. Encouraged by this example, several countries that were under the "Iron Curtain" feel they can claim more freedoms.
In East Germany, young students would gather in churches to listen to music and then go out in demonstrations to demand more rights. They were constantly watched and repressed by the police, but even so, the marches continued.
In November 1989, a German politician declared on TV that the Wall would be opened immediately. Despite wanting to say that it would be in a few days, the population understood that the opening would take place that same night.
In this way, thousands of Berliners took to the streets to destroy the Wall and reunite the city and the country.
Despite the differences between the two countries, Germany was reunited in record time. The Western part assumed all the economic, political and economic burdens of the German Democratic Republic.
The Fall of the Wall marked the end of the Cold War and accelerated the disintegration of the USSR.
Learn more about John Kennedy.
