Indonesia is officially the Republic of Indonesia, a country located in Southeast Asia. It is located between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It includes more than 17,000 14 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the largest island nation in the world and it has 1,904,569. largest country in the world with 735,358,270 XNUMX square kilometers (XNUMX XNUMX square kilometers). Nearly XNUMX million people, Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world and the largest Muslim nation in the world. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half the population.
An independent state is a state, a constitutional republic with an elected legislature. It has 34 provinces, of which five have special positions. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the second most populous city in the world. The country shares international borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor and the eastern part of Malaysia. Other neighboring countries include Singapore, Vietnam, the Philippines, Australia, Palau and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Although densely populated and densely populated, Indonesia has vast desert areas that support one of the world's highest ecosystems.
The Indonesian island has been an important commercial region since at least the 7th century when Srivijaya and later Majapahit traded with organizations from China and the Indian subcontinent. Local authorities gradually assimilated foreign influence from the first centuries, and even the Hindu and Buddhist empires flourished. Sunni traders and Sufi scholars introduced Islam, and Christianity was mainly introduced by European explorers. Although the Portuguese, French and British were sometimes disturbed, the Dutch were the major colonial powers for most of their 350 years on the islands. The idea of "Indonesia" as a nation-state emerged in the early 1920s, culminating in the proclamation of Indonesian independence in 1945. However, it was not until 1949 that the Dutch recognized the Indonesian monarchy after an armed conflict and communication between the two. / P>
Indonesia has hundreds of indigenous peoples and multilingual groups, the largest of which are Javanese. Shared identity is further reinforced by the motto "Bhinneka Tunggal Ika" ("Unity in Diversity" literally "many but one") defined in national language, racial diversity, religious diversity among the majority of Muslims and colonial history and insurgency. Indonesia's economy is 15th in the world in terms of GDP and 7th in GDP in PPP. Indonesia is a regional empire in Southeast Asia and is considered a central power in world affairs. The country is a member of various international organizations, including the UN, the World Trade Organization, G20, and a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the Association of Southeast Asia Nations (ASEAN), the East Asia Summit and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation.
Old story
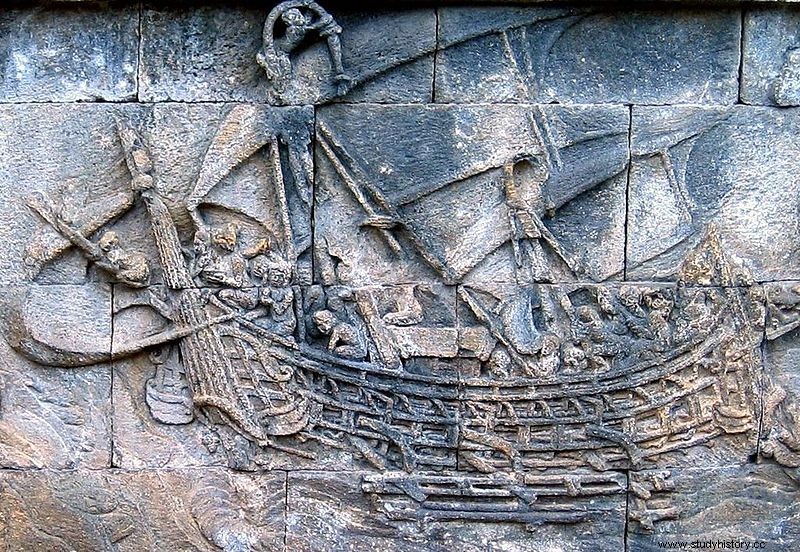

Remains of Homo erectus are now better known as "Java Man" and suggest that the Indonesian islands were inhabited between two million and 500,000 43,000 years ago. Homo sapiens reached the region around 2,000 8 BCE. The Australian people who make up the majority of the modern population and migrated to Southeast Asia from what is now Taiwan. They arrived in the archipelago around XNUMX BCE and confined the Melanesian natives to the Far East as they spread eastward. Appropriate agricultural conditions and careful study of rice cultivation in wetlands in the XNUMXs BCE allowed cities, towns and small empires to flourish in the first century AD. The archipelago with maritime routes promoted trade between the islands and other countries, including the Indian empires and the Chinese emperors, from many centuries BC. Since then, trade has shaped Indonesian history.
Government &Politics
Indonesia is a republic with a presidential system. After the fall of the new order in 1998, political and state structures implemented major reforms with four constitutional amendments. And revive the administrative, legal and judicial system. At their core is the transfer of power and authority to various regional structures while the unity of the coalition remains. The President of Indonesia is Head of State and Head of Government, Executive Director of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (National Tentara Indonesia, TNI) and Director of State Administration, Policy and Foreign Affairs. The president can serve two consecutive years for two consecutive years.
 The highest body represented at the national level is the People's Consultative Assembly (Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat, MPR). The main functions are to support, amend the constitution to open, replace the president in court, to formulate comprehensive national political frameworks. MPR has two houses Representative Council of the People (Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat, DPR) consisting of 575 members and the District Council of Representatives (Dewan Perwakilan Daerah, DPD) with 136 members. DPR adopts legislation and monitors the responsible branch. Changes since 1998 have greatly expanded its role in national governance, while the DPD is a new chamber for regional governance issues.
The highest body represented at the national level is the People's Consultative Assembly (Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat, MPR). The main functions are to support, amend the constitution to open, replace the president in court, to formulate comprehensive national political frameworks. MPR has two houses Representative Council of the People (Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat, DPR) consisting of 575 members and the District Council of Representatives (Dewan Perwakilan Daerah, DPD) with 136 members. DPR adopts legislation and monitors the responsible branch. Changes since 1998 have greatly expanded its role in national governance, while the DPD is a new chamber for regional governance issues.
Many civil disputes arise before the state court (Pengadilan Negeri). An appeal is heard in the High Court or Pengadilan Tinggi. The Indonesian Supreme Court (Mahkamah Agung) is the highest court in the jurisdictional court and deals with the final appeal and conducts a review of cases. Other courts include the Constitutional Court (Mahkamah Konstitusi) which deals with constitutional and political issues and the religious religion (Pengadilan Agama) which deals with combined cases on Islamic law (sharia). In addition, the Judicial Service Commission (Judicial Commission) monitors the performance of judges.
Parties and elections
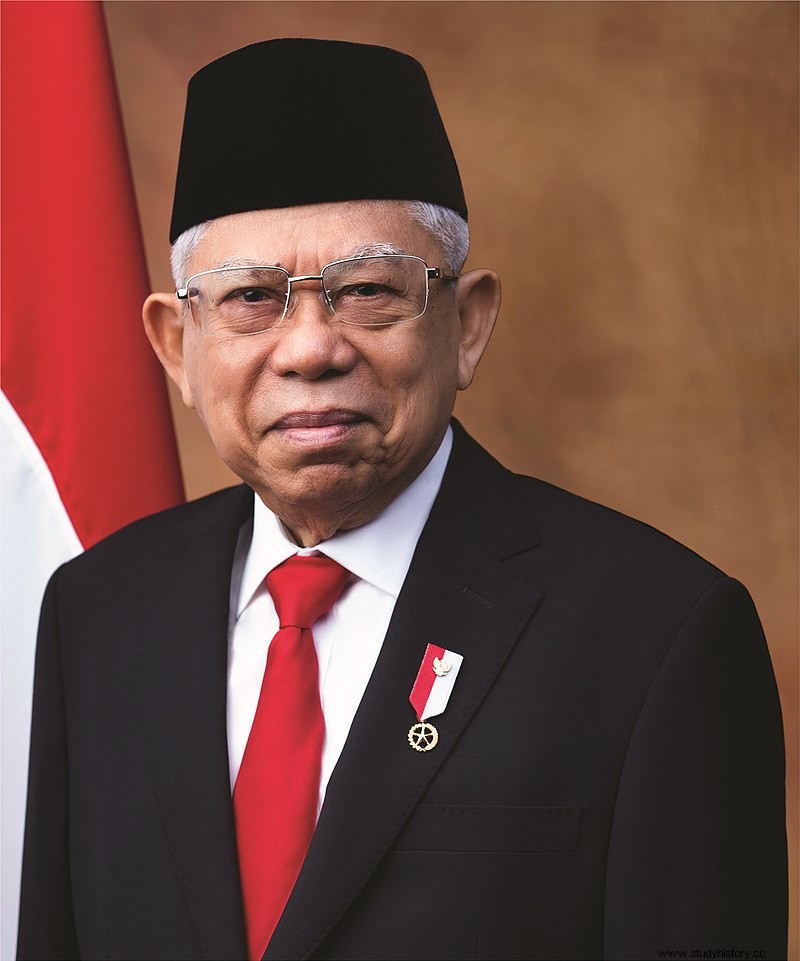 Since 1999, Indonesia has had a multiparty program. In all legislative choices since the fall of the new order. No political party has managed to win a majority of seats. The Indonesian Democratic Party for Fighting (PDI-P), which received the most votes in the 2019 election. Also the party of the acting president, Joko Widodo. Other prominent groups include the Working Group (Golkar), the Great Indonesia Movement Party (Gerindra), the Democratic Party and the Prosperous Justice Party (PKS).
Since 1999, Indonesia has had a multiparty program. In all legislative choices since the fall of the new order. No political party has managed to win a majority of seats. The Indonesian Democratic Party for Fighting (PDI-P), which received the most votes in the 2019 election. Also the party of the acting president, Joko Widodo. Other prominent groups include the Working Group (Golkar), the Great Indonesia Movement Party (Gerindra), the Democratic Party and the Prosperous Justice Party (PKS).
 The first parliamentary elections were held in 1955 to elect members of the DPR and the Constitution (Constituent Assembly). The last election in 2019 has led to nine political parties in the DPR, with a parliamentary margin of 4% of the national votes. At the national level, the Indonesian people did not elect a president until 2004. Since then, the president has been elected for a period of five years, as DPR-affiliated party members and DPD without party. Since the local elections in 2015, the election of leaders and mayors has taken place on the same day. In 2014, the Constitutional Court ruled that legal and presidential elections would be held simultaneously, from 2019.
The first parliamentary elections were held in 1955 to elect members of the DPR and the Constitution (Constituent Assembly). The last election in 2019 has led to nine political parties in the DPR, with a parliamentary margin of 4% of the national votes. At the national level, the Indonesian people did not elect a president until 2004. Since then, the president has been elected for a period of five years, as DPR-affiliated party members and DPD without party. Since the local elections in 2015, the election of leaders and mayors has taken place on the same day. In 2014, the Constitutional Court ruled that legal and presidential elections would be held simultaneously, from 2019.
Foreign Relations
Indonesia has 132 foreign embassies including 95 embassies. The country adheres to what it calls a "free and effective foreign policy" that seeks to participate in regional affairs in relation to size and location, but to avoid involvement in conflicts between other countries.
Indonesia was a major battlefield during the Cold War. Many attempts by the United States and the Soviet Union and the People's Republic of China to a certain extent culminated in the coup attempt in 1965 and the subsequent unrest that led to duplication of foreign policy. Silent adaptation to the Western world while maintaining a non-violent stance has characterized Indonesia's foreign policy ever since. Today, it maintains a close relationship with its neighbors and is a founding member of the Association of Southeast Asia Nations (ASEAN) and the East Asia Summit. Like most Muslims, Indonesia has no ties to Israel and has supported Palestine. However, observers have pointed out that Indonesia has ties to Israel, although this can not be done discreetly.
 Indonesia has been a member of the UN since 1950 and is a fundamental member of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). Indonesia has from time to time signed an agreement with ASEAN Free Trade Area, Cairns Group, World Trade Organization (WTO) and OPEC member. During the conflict in Indonesia - and Malaysia, Indonesia withdrew from the UN as a result of its election to the UN Security Council, although it returned 18 months later. It is the first time in UN history that a member state has tried to withdraw. Indonesia has been a recipient of aid and development since 1966, and more recently launched its first foreign aid program in late 2019.
Indonesia has been a member of the UN since 1950 and is a fundamental member of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). Indonesia has from time to time signed an agreement with ASEAN Free Trade Area, Cairns Group, World Trade Organization (WTO) and OPEC member. During the conflict in Indonesia - and Malaysia, Indonesia withdrew from the UN as a result of its election to the UN Security Council, although it returned 18 months later. It is the first time in UN history that a member state has tried to withdraw. Indonesia has been a recipient of aid and development since 1966, and more recently launched its first foreign aid program in late 2019.
Geography &Geology
Indonesia is located between 11 ° S and 6 ° N, 95 ° E and 141 ° E. It is the largest island nation in the world and extends 5,120 miles (3,181 mi) from east to west and 1,760 miles (1,094 mi) from north to south . The Ministry of Maritime Liaison and Investment estimates that Indonesia has 17,504 16,056 islands (6,000 XNUMX registered in the UN) spread across the equator, of which about XNUMX is inhabited. The largest are Sumatra, Java, Borneo (shared with Brunei and Malaysia), Sulawesi and New Guinea (shared with Papua New Guinea). Indonesia shares world borders with Malaysia on Borneo and Sebatik, Papua New Guinea on the island of New Guinea, and East Timor on the island of Timor, and maritime borders with Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, the Philippines, Palau and Australia.
At 4,884 meters, Puncak Jaya is the highest peak in Indonesia, while Lake Toba in Sumatra is the largest lake with an area of 16,024 km1,145 (2 square meters). The main rivers in Indonesia are in Kalimantan and New Guinea and include the rivers Kapapuas, Barito, Cambamber, Sepik and Mahakam. They act as communication and transport links between the rivers on the island.
Indonesia is sometimes relatively unstable, making it the site of many common volcanoes and earthquakes. It is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire where the Indo-Australia Plate and Pacific Plate are located at the bottom of the Eurasian plate, where they melt about 100 miles (62 miles) deep. A series of volcanoes cut through Sumatra, Java, Bali and Nusa Tenggara, and then to the cold Maluku Islands northeast of Sulawesi. Of the 400 volcanoes, around 130 are active. Between 1972 and 1991, there were 29 volcanic eruptions, mainly in Java. Volcanic ash has made agricultural conditions unpredictable in some areas. However, it also led to fertile soil, which is a factor in historically supporting the overpopulation of Java and Bali.
 A massive supervolcano erupted in today's Tobasjø around 70,000 1815 BC. It is believed to have created volcanic winters and cooling of the climate and to have led to the development of genes for human evolution, although this is still controversial. The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1883 and the Krakoa eruption of 92,000 were among the largest in recorded history. The first in 1816 killed 36,000 people and made an umbrella of volcanic ash that spread and covered parts of the island and formed large parts of the northern hemisphere outside the summer of 2004. The latter produced the largest noise in recorded history and resulted in the deaths of 2006 XNUMX people who a result of the actual explosions and tsunamis, which had a further impact on the world in the years following the incident. Recent disasters caused by earthquake activity include the earthquake in the Indian Ocean in XNUMX and the earthquake in Yogyakarta in XNUMX.
A massive supervolcano erupted in today's Tobasjø around 70,000 1815 BC. It is believed to have created volcanic winters and cooling of the climate and to have led to the development of genes for human evolution, although this is still controversial. The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1883 and the Krakoa eruption of 92,000 were among the largest in recorded history. The first in 1816 killed 36,000 people and made an umbrella of volcanic ash that spread and covered parts of the island and formed large parts of the northern hemisphere outside the summer of 2004. The latter produced the largest noise in recorded history and resulted in the deaths of 2006 XNUMX people who a result of the actual explosions and tsunamis, which had a further impact on the world in the years following the incident. Recent disasters caused by earthquake activity include the earthquake in the Indian Ocean in XNUMX and the earthquake in Yogyakarta in XNUMX.
 From the seventh century AD. the sea kingdom Srivijaya flourished as a result of trade and the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism. Between the eighth and tenth centuries CE, Buddhist monarchs Sailendra and Hindu Mataram emperors flourished and settled in central Java, leaving behind large religious monuments such as Saoborur of Sailendra and Prambanan of Mataram. The Hindu empire Majapahit was established in eastern Java in the late 13th century, and under Gajah Mada, its influence permeated many parts of present-day Indonesia. This period is often referred to as the "golden age" in Indonesian history.
From the seventh century AD. the sea kingdom Srivijaya flourished as a result of trade and the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism. Between the eighth and tenth centuries CE, Buddhist monarchs Sailendra and Hindu Mataram emperors flourished and settled in central Java, leaving behind large religious monuments such as Saoborur of Sailendra and Prambanan of Mataram. The Hindu empire Majapahit was established in eastern Java in the late 13th century, and under Gajah Mada, its influence permeated many parts of present-day Indonesia. This period is often referred to as the "golden age" in Indonesian history.
The earliest evidence of Islamized people on the islands dates back to the 13th century north of Sumatra. Other parts of the island gradually converted to Islam, and it was the dominant religion in Java and Sumatra in the late 16th century. For the most part, Muslims cover up and mix with existing cultural and religious influences, forming a prominent Islamic state in Indonesia, especially in Java.
Current issues and events in Indonesia
-Indonesia's new criminal law. Indonesia has been working to renew the penal code for colonial times for decades.
-Growing discrimination and attacks on LGBT people.
-No UN access to West -Papua.
-Increased religious intolerance.
-The Minister of Defense is involved in the harassment.
Problems include deforestation (many of which is illegal) and associated forest fires that cause heavy smoke in the western parts of Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore, excessive use of maritime resources and environmental problems related to urbanization and economic development, including air pollution and traffic.
