Cuba , whose official name is the Republic of Cuba, is an island located in the Caribbean Sea.
The country played a crucial geopolitical role in the 20th century, as it was the only socialist state geographically closest to the United States.
General Data
- Name :Republic of Cuba
- Capital :Havana
- Currency :Cuban Peso
- Government regime :Unitary Leninist-Marxist Socialist Republic
- President :Miguel Diaz Canel (since April 19, 2018)
- Language :spanish
- Population :11 million (2017)
- Area :110,861 km 2
- Demographic density :102 inhabitants per km 2 .
- Cities :Havana, Santiago de Cuba, Santa Clara, Varadero.
Flag

The Cuban flag is made up of five horizontal stripes:three blue and two white. On the left we have a red triangle with a white star.
It was created in 1849 by General Narciso López (1797-1851) and has Masonic origins. However, it was only adopted as the country's official flag in 1902 when Cuba became an independent country.
The blue, white and red colors are associated with the ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity and have inspired countless national pavilions around the world.
The triangle was inspired by the same geometric shape that Freemasons use to represent divinity. The star, in turn, would represent the solitude of an independent country as the great ideals of humanity.
Map
Cuba is located in the Caribbean Sea. The island of Cuba is the main one, followed by the Isle of Youth and more than 350 islets are part of the republic.
To the north is the United States; to the south, Jamaica; to the east, Mexico; and to the west, islands such as Turco and Caicos.
Weather
Cuba's climate is tropical, humid and with temperatures ranging from 18º to 31º during the year. It has two seasons:the dry season from November to April and the rainy season from May to September.
Due to its location, the country is a victim of hurricanes, especially in the months of August to October, when the Caribbean storms are more frequent.
History
Cuba was inhabited by Taino Indians and Ciboneys, like most Caribbean islands. After the arrival of the Spaniards, due to diseases and wars, the indigenous population practically disappeared.
In this way, the Spaniards imported enslaved Africans to work on the sugar mills and tobacco plantations, the two great products of the island.
In addition, it was an important port for the redistribution of enslaved blacks and a stop for Spanish galleons crossing the Atlantic.
That's why Cuba was considered the "pearl of the Caribbean", the "jewel in the Crown" and was one of the most prosperous colonies of the Spanish Empire.
Its economy was so prosperous that Cuba opened the first railway line in 1837, thirteen years before Spain.
See also:Spanish AmericaIndependence
Unlike the Spanish colonies in South and Central America, Cuba would not become independent until the end of the 19th century.
The Cuban process would also have strong US influence through arms, politics and money.
This was due to several factors. First, the Spanish Crown managed to stifle any attempt at revolt, either through arms or through economic concessions. Second, the small size of the island made surveillance more efficient.
For its part, the American government had declared the Monroe Doctrine in 1823, which warned that the American continent would be for Americans only, not accepting the interference of European powers.
Likewise, in 1852, the American government makes a proposal to buy Cuba from the Spanish government, but the offer is refused. Later, the US insisted on acquiring the island twice more, but Spain never accepted.
In 1868, a group of Cuban revolutionaries carried out a series of uprisings and demanded the recognition of independence by Spain. The result is more soldiers being sent to the island.
In 1895, led by José Martí (1853-1895), a new attempt at separation was made, without success. Meanwhile, the Americans were campaigning in the press against Spain and welcoming Cuban exiles. This would all help to prepare public opinion for an imminent war against the European country.
See also:Independence of Spanish AmericaSpanish-American War
The pretext would come on January 25, 1898 when an explosion occurs on the American ship "Maine" , anchored in the port of Havana, killing 16 Americans.
The American government quickly accused the Spaniards of being responsible for the attack and declared war on the country. At the same time, they take advantage of attacking the Philippines and other Spanish possessions in the Pacific.
Without being able to face a more powerful enemy and sustain two battle fronts, the Spaniards lost their territories to the United States in the Caribbean and Pacific
American Protectorate
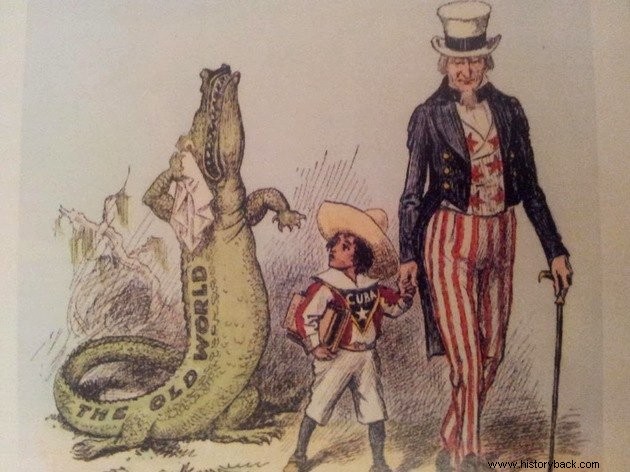

After the end of the war, the United States forced the Cuban government to accept the Platt Amendment in the 1903 Constitution.
The Platt Amendment provided:
- land assignment to the United States;
- American military intervention in Cuba when its sovereignty was threatened;
- prohibition of treaties with other countries;
- limitation of public debt and foreign borrowing.
The United States now controls the island's economic activities, in addition to obtaining the concession for the Guantánamo region. The Platt Amendment would not be repealed until 1934.
Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution, led by Fidel Castro, Che Guevara, Camilo Cienfuegos, among others, set the world on fire in the middle of the Cold War.
A group of Cubans, who opposed the government of dictator Fulgencio Batista, managed to overthrow him and take power in 1959. The United States arms dissidents and tries to invade the island through the Bay of Pigs, but they are defeated.
Without its main buyer and investor, Cuba accepts the help offered to it by the Soviet Union. In this way socialism is installed on the Caribbean island.
The country managed to eradicate illiteracy and made health a universal good. However, it persecuted its opponents, censored newspapers and prohibited its inhabitants from leaving the island.
See also:Cuban RevolutionEconomy
When it was colonized by the Spanish, the island became a major producer of sugar, rum and tobacco.
After independence, due to the influence of the United States, part of the economy remained agricultural. However, there was a boost from the service sector with the construction of casinos, hotels, vacation homes for wealthy Americans.
After the Cuban Revolution in 1960, the country guaranteed a share of the Soviet market for its products and received oil, machinery and parts.
According to the US Department of Commerce, in 2016, US exports to Cuba amount to less than US$400 million a year. The most exported product is food.
On the other hand, the volume of Cuban exports to the US is not known, because, officially, they do not exist. The ensuing trade embargo by the United States prohibits any American investment.
In 2000, with Hugo Chávez, he began to receive oil and financial aid from Venezuela. However, in 2013, with the drop in prices, the country suffered again from the economic crisis.
Upon assuming the government in 2006, Raúl Castro, Fidel's brother, promotes a series of reforms that include trade liberalization. In this way, it is now possible to:
- have their own business and 10% of the active population already does it;
- foreign companies invest and hire Cubans, in the Mariel Special Economic Development Zone;
- buying and selling real estate, although there are many restrictions. Despite this, in two years, 40,000 houses were traded.
End of the American Embargo?
US President Barack Obama tried to end the economic embargo, but the measure was not approved by Congress.
Anyway, Obama visited the island, reopened the American embassy, allowed the resumption of commercial flights between both countries, among other measures that would facilitate the rapprochement of the two countries.
However, with the election of Donald Trump to the White House, many of those resolutions have already been undone.
Culture

Because of miscegenation and the meeting of cultures, Cubans have developed a culture rich in music, poetry and literature.
Music
Cuban rhythms like the guajira , the parsley , the mambo, a conga, thebolero gained notoriety. Due to the North American influence, several artists took their art to centers like Hollywood and New York and from there to the whole world.
Any list of Cuban musicians will always be incomplete due to the quality, quantity and international fame they have achieved.
From the "queen of salsa" Célia Cruz (1925-2003), to the American rapper of Cuban origin Pitbull (1981), passing jazz instrumentalists such as Mario Bauzá, Cuban musicians conquered the world with their talent and originality.
Let's name just a few:
| Ruben González | pianist | Compay Second | singer and guitarist |
| Celia Cruz | singer | Paquito D'Rivera | clarinetist and saxophonist |
| Drink Valdez | composer and pianist | Arturo Sandoval | trumpeter |
| Israel 'Cachao' López | double bass player | Chucho Valdés | pianist |
| Gloria Estefan | singer | Omara Portuondo | singer |
| Jon Secada | singer | Ibrahim Ferrer | singer |
| Ernesto Lecuona | pianist | Leo Bouwer | guitarist |
| Pablo Milanés | composer | Sílvio Rodriguez | composer |
In 2004, the Brazilian dance company Grupo Corpo performed the choreography "Lecuona " based on the work of the Cuban composer.
Literature
The island of Cuba was lavish with writers and poets who sang it in prose and verse. Despite never having been awarded a Nobel Prize, Cuban literature has enriched the Spanish and universal vocabulary.
Some examples are José Martí, Guillermo Cabrera-Infante, Alejo Carpentier, Pedro Juan Gutierrez, etc.
Dance
The dance has developed both on a popular level with the conga , the parsley , the mambo , the cha cha tea and on the classical side being the Ballet Nacional de Cuba, one of the great ballet companies in the world.
Since 1959, the company has been directed by dancer Alicia Alonso (1921) and has performed in several countries, including Brazil.
Religion
Most of the country declares itself to be Catholic Christian. However, as happened in Brazil, the religion brought by the enslaved people merged with Catholicism, generating santeria .
As in Candomblé, the orixás were identified with Catholic saints and in the terreiros you can see the presence of Catholic images next to atabaques and animal sacrifices.
Although the regime declared itself atheist and incorporated the communists' criticism of religion, the fact is that Cuba was one of the few socialist-oriented countries that kept its diplomatic representative in the Vatican.
Currently, neo-Pentecostal religions are also growing in Cuba.
Curiosities
- In 1999, Fidel Castro founded the Latin American School of Medicine with the aim of promoting study in the region. It is estimated that over 500 Brazilian students have already passed through the institution.
- At least two "drinks" of Cuban origin have won bars around the world:cuba libre and daiquiri.
- Due to the success of the Brazilian soap opera "Vale Tudo" , by Gilberto Braga, in Cuba, the word "taste" has become synonymous with restaurant. This is because the character Raquel, played by actress Regina Duarte, owned an establishment called "Paladar" .
Read more :
- Cold War
- Missile Crisis
- John Kennedy
- North American Imperialism
- Spanish Colonization
