Sub-Saharan Africa is the political-geographical term applied to describe the countries of the African continent located in the region south of the Sahara desert.
It is one of the poorest regions in the world with high rates of infant mortality, illiteracy and low life expectancy.
Countries
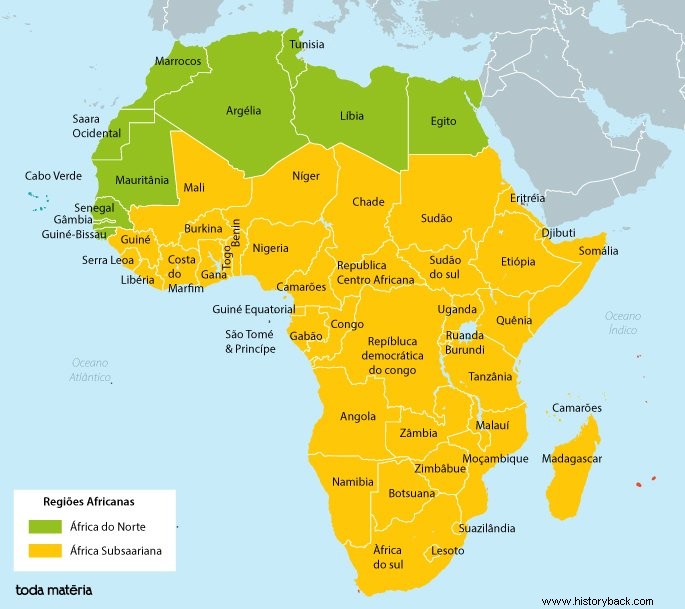
Sub-Saharan Africa is made up of the following countries:
- South Africa
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Shrimps
- Cape Verde
- Chad
- Congo
- Ivory Coast
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Comoros Islands
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauricio
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Kenya
- Central African Republic
- Rwanda
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Population
World Bank data indicate that this is the poorest region on the planet. At least 41% of the population, out of more than 1.2 billion people, live in the urban region. The income per capita is US$925 and life expectancy at birth is 56 years.
To understand the difference, let's compare these data with those from Brazil. According to the World Bank, the life expectancy of Brazilians at birth is 76.6 years and the per capita income reaches US$ 6,796.
27 of the 30 lowest HDI countries are located in this region, making poverty almost endemic.
Economy
Extractivism is the main source of income in Sub-Saharan Africa. This piece of the African continent holds 7% of the world's oil reserves and important reserves of phosphate, copper and cobalt.
Tourism is also a developing industry, as Tanzania's beaches and Kenya's nature reserves, for example, attract European and American tourists.
Sub-Saharan Africa has been receiving heavy investments from the Chinese in search of securing raw materials and, above all, land to feed its population.
The region experienced incredible growth in the first decades of the 21st century due to the increase in raw material exports.
Currently, some countries such as Nigeria and Egypt have been showing an increase in their level of industrialization and have started to enter more into the international market.
See also:Economy of AfricaHistory

Sub-Saharan Africa is considered the cradle of the human race, because in the region called East Africa the genus Homo emerged. . The evidence is in tools collected by archaeologists and marks the beginning of the Paleolithic.
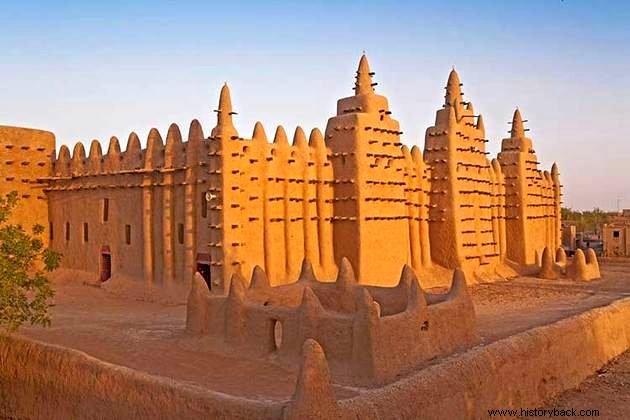
The region was also home to large kingdoms such as Mali (XIII-XVI), which monopolized the salt trade. This allowed them to trade the product through trans-Saharan routes and obtain products in iron, horses and crockery.
As it was an Islamic kingdom, several mosques were erected and currently, Timbuktu's temples have been declared a World Heritage Site.
Geography
Africa is the most stable terrain on Earth. The continent has remained in the same position for about 550 million years and most of it is made up of an enormous plateau.
Close to the equator is an area with tropical rainforests, surrounded by the savannah that occupies most of sub-Saharan Africa.
Further south of the continent is the Kalahari Desert, which extends to the coast of the Atlantic Ocean.
Weather
The climate is influenced by the Equator, although there are temperate microclimates in the highlands. The region is rainy and with precipitation typical of humid forests.
Since the last Ice Age, there has been a climate-imposed separation between the North and Sub-Saharan Regions. The severity of the climate is interrupted only by the River Nile.
Sub-Saharan Africa, compared to the north of the Sahara, was isolated and practically did not receive the influence of Arab culture and Islam.
Geology
The rocks typical of this region solidified during the Earth's first eruption cycles and today represent the main source of the economy, based on the mining of gold and diamonds. The region is also rich in copper and chromium, as well as oil.
See also:General aspects of Africa:map, countries and economyLanguage and Religion
There are at least 600 languages spoken in Sub-Saharan Africa, most of which are of Bantu origin. There is also the influence of European colonization and, therefore, there are nations that speak Portuguese, French and English.
Most countries are Christian, concentrating 21% of the world's Christians. However, there are a large proportion of Muslims and countries, such as Nigeria, where the population is practically divided between the two faiths.
There are also those who practice traditional African animist religions.
AIDS

In addition to extreme poverty, which mainly affects countries ravaged by constant civil wars, Africa suffers from an AIDS pandemic that devastates the region.
The productive capacity of countries has been put in check due to the immense number of orphans of parents who die very young due to the consequences of the disease.
South Africa, for example, has 4 million AIDS orphans. In Malawi, the scene is repeated and several children and adolescents are already heads of families.
Among the justifications for the contamination rate is sexual exploitation and the treatment given to women, who are considered inferior.
Read more :
- North Africa
- Countries of Africa
- Decolonization of Africa
