Of all the recorded incidents in the past, one of the most effective series is the World Wars. All of us know that history books are about a couple of world wars that led to many changes before and after.
This post is focused on bringing the history of two world wars, its occurrences and global consequences briefly.
World War I
World War I took place between July 28, 1914 and November 11, 1918. Based on the course of the war, there were three groups of nations around the world. Two groups of nations fought each other in the war, while the third set of countries chose to take a neutral stand.
Who was involved?
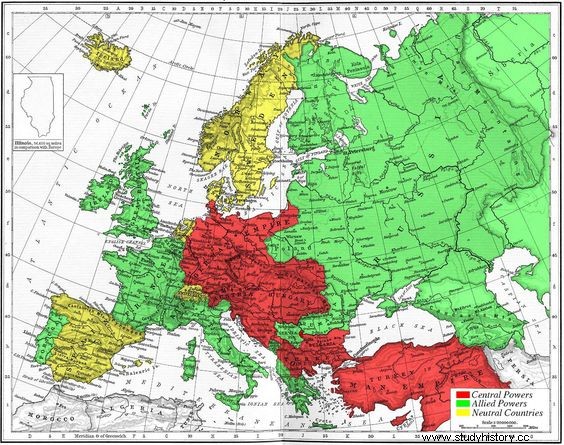
For a better understanding, let's see how the boundaries were divided based on the three sets of land:
First, the central power was constituted by the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, Turkey and Bulgaria. These countries were physically located in the central part of the continent's countries. They are marked in red in the image above.
Second, the Allied powers had lands from other continents and were physically located in the outer region of the European continent. That is also why they became known as the Allied Power. It was made up of Italy, France, Great Britain, Ireland, Portugal, Greece, Russia, Siberia, Japan and the United States. These are marked in green.
Third, the neutral powers were constituted by Spain, the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden, Norway. These are marked in yellow.
How did the war begin?
Archduke Franz Ferdinand was heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire. When he visited the Bosnian capital Sarajevo with his wife Sophie on June 28, 1914, the couple was shot dead by Gavrilo Princip. Princip was a Serbian nationalist. This naturally aroused the Austro-Hungarian authorities. This event marked the basis for the beginning of the First World War.
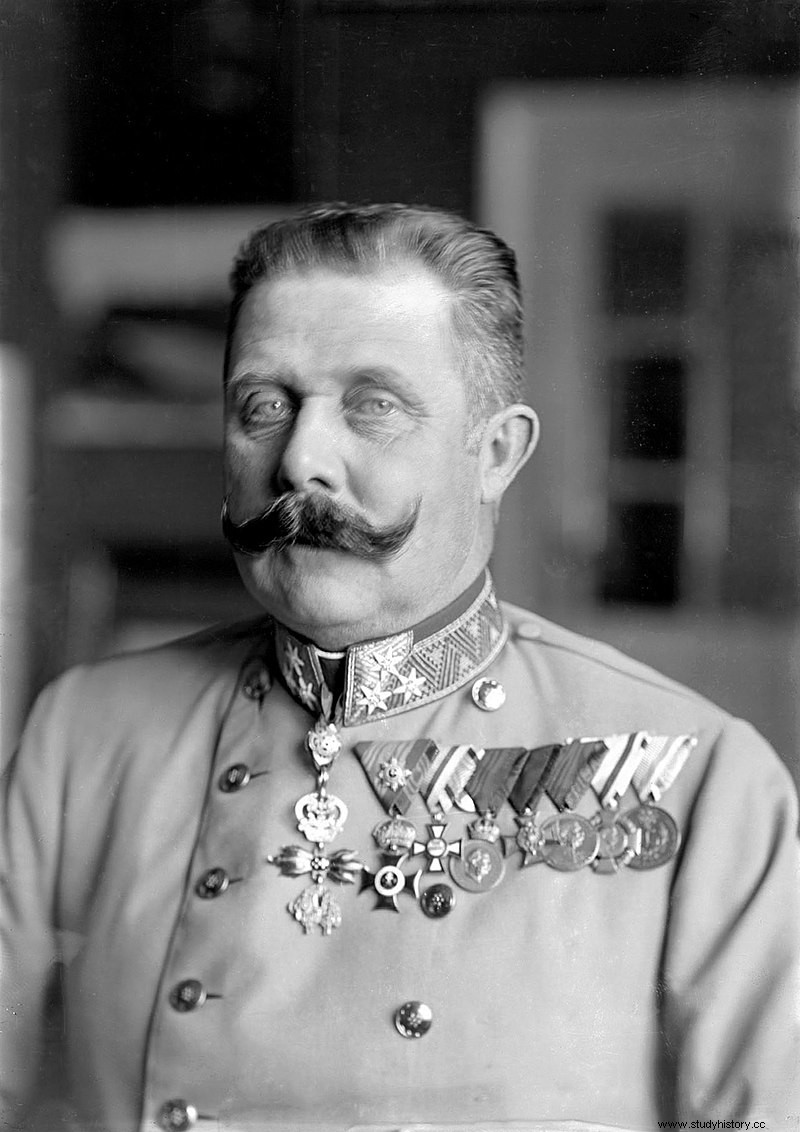
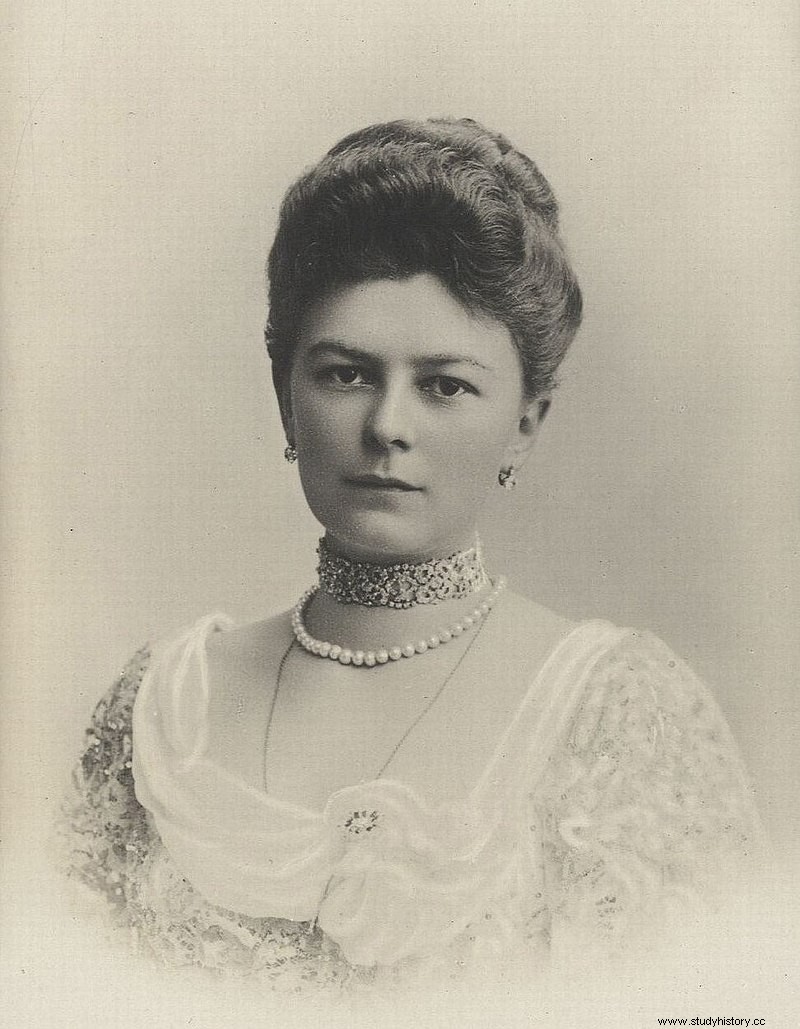


The heir and his wife went to inaugurate the State Museum and observe the military maneuvers. Due to the then uncomfortable political situation between Austria and Serbia, his wife is said to have followed him. The tension has been the result of years of fighting between the European nations to gain supremacy over the others.
In fact, about an hour before the gun was fired, the couple missed a grenade attack. It was planned by a group of six assassins on their car. They were armed with supplies from a Serbian citizen. The political goal of this attack was Serbia's desire to acquire a South Slavic province. This part of Bosnia was annexed by Austria-Hungary from the Ottoman Empire.
How did the war develop?
Leading towards the declaration of war:"July -crisis"
The Austro-Hungarian authorities were agitated after the attack on the royal couple. This motivated a series of anti-Serbian riots in Sarajevo. As a result, a number of Serbs were imprisoned and injured. Bosnian Serb and Serbian-owned buildings were damaged. That's how the "July crisis" began.
There was political unrest among Austria-Hungary, Germany, France, Russia and Britain. Although Austria was clear on the Serbian involvement in the attack, they lacked any clear evidence of it. Austria secretly sought the support of the powerful Russia's supporter of Serbia, Emperor Wilhelm II. On July 5, the German leader agreed to issue a "blank check" with the promise of supporting the dual monarchy in the emergence of a war. So too, Serbia was convinced that Austria was ready for a war. Therefore, the government ordered the military to be ready and appealed for Russia's assistance.
Consequently, on July 23, 1914, Austria-Hungary delivered the "July Ultimatum" to Serbia. It was a list of ten demands that were made to deliberately provoke them. Thus, most of them were unacceptable. Nevertheless, Serbia agreed to everything except the fifth and sixth points. Because they were related to having Austria-Hungary investigate the Serbian officials.
After this, on July 25, both Serbia and Russia ordered their military to stand up against Austria-Hungary. Then, on July 28, 1914, exactly one month after the assassination attempt, the Austro-Hungarian government declared war on Serbia. A week later, Russia, Serbia, Belgium, France and the United Kingdom faced Austria-Hungary and Germany. World War I had begun.
Beginning of War
The war involved many battles between the Allies and the Central Powers. Germany followed the plan of Field Marshal Alfred Von Schlieffen and therefore fought the war on two fronts. They were against France in the west and Russia in the east. The strategy of the German battle order was to place 80% percent of the army in the West. So they turn off France via Belgium and then copy it with Russia in the east.
On August 4, 1914, German troops invaded the city of Liege and crossed the border into Belgium. To begin with, the Germans succeeded in advancing along the western front. At the Battle of the Borders, nearly 260,000 27,000 people were wounded and XNUMX XNUMX of them were executed. However, due to the lack of micro-control of the army commanders, they had the freedom to carry out the broad instructions given to them in their own way. While Von Kluck used this freedom not to obey orders, the French army took advantage of this gap to win over the German invasion of the West.
Kampene i Vesten
Consequently, on September 6, 1914, the first battle of the Marne was fought between the Franco-British army and the German army. The German army invaded northeastern France. But the Allied army drove the Germans back north of the Aisne River.

The battle of Verdun was fought between February 21 - December 18, 1916. It caused a lot of bloodshed and is known for its brutality. It was fought for 10 months in a row, which made it one of the longest battles. The Germans chose the city of Verdun in France as their destination because it was prominent, located on the western front and already had a political history.
The battles in the east
While the above battles were part of the Western Front, the Battle of Tannenberg took place on the Eastern Front at the end of August 1914. Russia attempted to invade German-held parts of Prussia and Poland. But the army was stopped by Allied forces in Germany and Austria. Although the Germans won this battle, it came at the expense of devoting a larger portion of their troops to the Eastern Front. In the end, it caused their loss at the Battle of the Marne as well.

Therefore, Schlieffen's plan did not work. The Germans had to mobilize the troops in different proportions to face the simultaneous battles on both fronts from time to time.
During the years from 1914 to 1916, the Russian army failed to break through the German lines. This led to political and economic instability, which led to a shortage of food and necessities. As a result, the people of Russia came together for the Russian Revolution, led by Vladimir Lenin and the Bolsheviks in 1917. As a result, Russia was forced to end the struggle. It is officially known as a ceasefire. Thus, they reached a ceasefire with central powers in 1917.
Battle of Gallipoli
Meanwhile, the Ottoman Empire took the side of the central government in the war of November 1914.
The United States has joined the war
After the Russian forces left in World War I, Germany only had to fight against the Western Front. Initially, at the beginning of the war, the United States was neutral. While during the war, Germany became aggressive over neutral ships and tanks. In 1915, they declared the waters around the British Isles a war zone. The German submarines sank many commercial and passenger vessels.
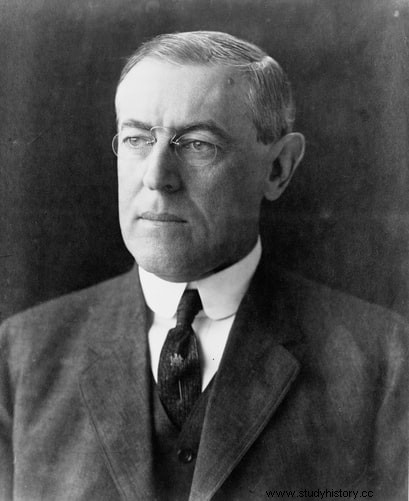
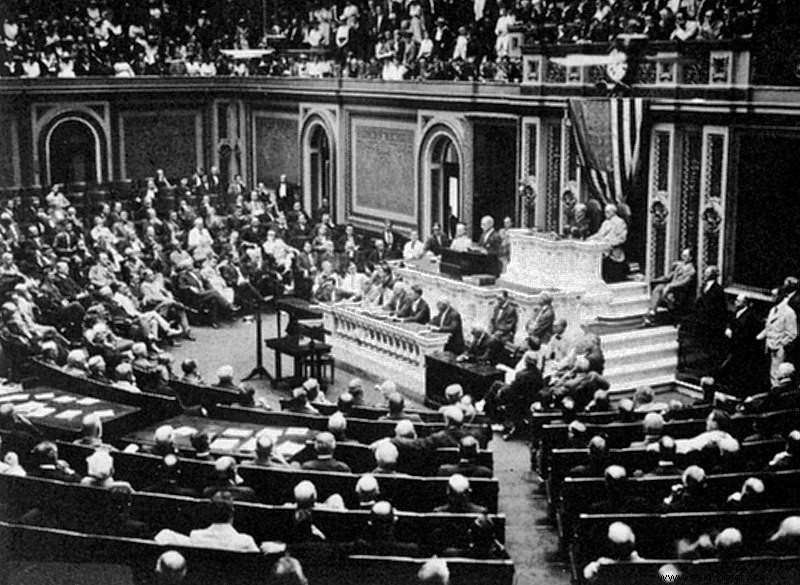
American ships were no exception to this brutality. An American ship named Lustania was sunk by the German navy on May 7, 1915. This naturally violated international submarine warfare laws. Despite the loss of 128 citizens on board, then-US President Woodrow Wilson only warned the country to comply with the law. Although Germany first agreed to this, they resumed unlimited warfare in January 1917, expecting Britain to surrender.
It was rather an indirect invitation to the United States to join the war. Since the president had already mentioned that they would not tolerate such illegal warfare, Germany was waiting for entry. On April 2, 1917, Wilson appeared before the Congress Party and declared war on Germany. Four days later, on April 6, the US Congress declared war on Germany.

How did the war end?
When history has countries going out and coming in, let's see how this ended. Germany won a few battles recently after Russia left the war. They strengthened their presence on the Western Front, but only until the United States set foot on the battlefield.
Second Battle of Marne
On July 15, 1918, the last battle was called by German forces against the French troops. With the help of American and British forces, the French army succeeded in pushing the Germans back and carried out a successful counterattack after three days. Therefore, this turned the table and the Allied powers were able to regain much of France and Belgium in the following months.
Although Turkey won Gallipoli, the Ottoman Empire collapsed after the Arab uprisings. This led to the Empire's ceasefire and to the signing of a treaty with the Allied Powers in October 1918. Not very recently, Austria-Hungary also reached a ceasefire on November 4 due to internal nationalist movements. Eventually, Germany was forced to declare an end to the war due to the surrender of its allies and lack of resources. World War I ended when Germany sought a ceasefire on November 11, 1918.
Versailles Treaties
In 1919, the Paris Peace Conference was held, followed by the Treaty of Versailles signed on 28 June 1919 by the Allies and Central Powers. It was exactly five years after the assassination of the Austrian royal couple. The document contained many provisions. Separate treaties were signed by each of them. The controversial one is - the "War Guilt" clause signed by central powers. It was stated that they were responsible for all losses and damage during the war.
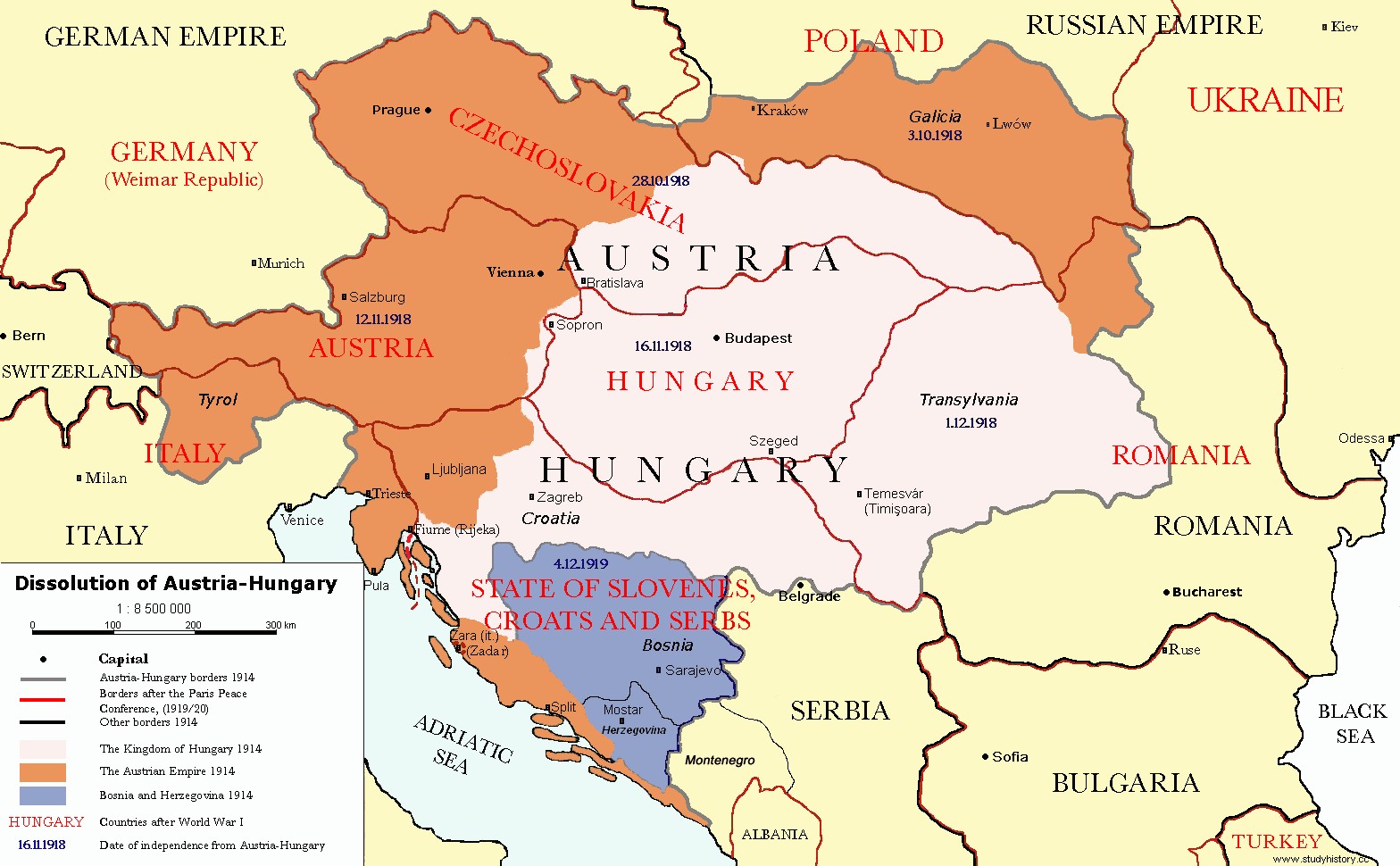

The borders were redrawn and as a result of the Russian Revolution the monarchy ended and Russia became a republic nation known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR).
World War
World War I seems to have ended in a peace treaty. But it was hard on Germany by forcing it to disarm, pay France compensation, give up some land and sign to take responsibility for the damage caused. While President Wilson believed that his fourteen points should be implemented, he also believed that Germany should not be blamed or punished for causing the damage. Thus, this "unfair treaty" is one of the reasons for the sequel.
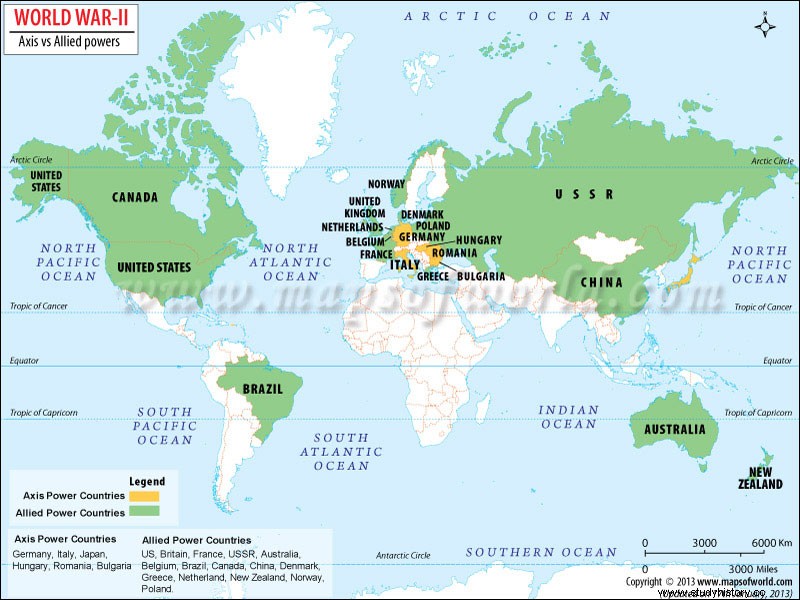
In 1933, Adolf Hitler became Chancellor of Germany. He quickly came to power and became a notorious dictator in 1934. He firmly believed that for a pure German race (which he called "Aryans") to strive, he would expand the living space and conquer the borders. Therefore, he secretly armed the country in the 1930s and signed pacts with Italy and Japan. Although it violated the Treaty of Versailles, he went ahead and even annexed Czechoslovakia in Austria in 1938. America and Britain were too busy handling their internal policies to respond to this aggressive move. This is how the three most important "axis powers", namely Germany, Italy and Japan, came into being.
In August 1939, Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union and Hitler signed a German-Soviet non-aggression pact. And then Hitler began invading Poland on September 1, 1939, from the west, marking the beginning of World War II. But France and Britain had already promised to save Poland in the event of such an invasion. Therefore, they both declared war on Germany on September 3. Subsequently, the Soviet Army attacked Poland from the east, making it easy for Germany to conquer. According to the Nonaggression Pact, Poland was divided between the Soviet Union and Germany to govern.
World War II in the West
1940 - 1941
On April 9, 1940, Germany invaded Norway and Denmark at the same time. Furthermore, on May 10, they swept through Belgium and the Netherlands, which is referred to as the "Lightning War". France was under pressure due to continuous attacks by the German forces. The Italian dictator Benito Mussolini took advantage of the situation and signed another pact with Germany called the "Steel Pact" on May 22, 1939. From then on, they waged war against Britain and France.

Due to strong opposition, France surrendered to Germany on June 16 and sought a ceasefire. Under the French government formed by Marshal Phillip Petain, Germany gained control of part of France. Now the next destination was Britain in the West. But geographically, the continent was divided by water, which made the task quite difficult for the Germans.
Nevertheless, they developed a new method of attacking them by bombing from planes. From September 1940 to May 1941, a number of German planes dropped bombs on Britain, affecting civilians and causing serious damage. But in the Battle of Britain, the Royal Air Force (of Great Britain) won over the German Air Force. Due to a lack of resources, Prime Minister Winston Churchill sought help from the United States through the Lend-Lease Act passed by Congress in 1941.

1941 - 1942
Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria had joined the Axis powers in early 1941. After the conquest of a large number of countries in the west, Germany decided to implement its strategy. While it was a non-aggression pact with the Soviets, Hitler's actual intention was also to annex Soviet land in order to expand his territory. Finally, on June 22, 1941, Operation Barbarossa was executed for invading the Soviet Union. Although Russia was large in size, their aviation technology was behind Germany's. Despite such backlogs and unique warfare for which they were not prepared, they defeated Germany.
XNUMX. world war in the pacific
1943 - 1945
Germany was left to fight only Britain in Europe. While another Axis power, Japan attacked China in the Pacific. Because it aimed to expand the border with Central Asia and the Pacific. Thus, it took on China in 1937 and the United States in December 1941. On December 7, 1941, about 360 Japanese planes attacked the US Navy base in Hawaii at Pearl Harbor. This prompted the United States to declare war on Japan on December 8. Naturally, Japan and other Axis powers declared war on the United States 

The Battle of Midway in June 1942 saw the victory of the Allied forces after a long defeat of Japan with the emergence of the United States. In the years that followed, from August 1942 to February 1943, Allied naval forces attacked Japan vigorously. As history repeats itself, the listing in the United States once again turned the tables and helped Allied powers move closer to the invasion of mainland Japan.
End of War
In November 1942, the Soviets launched a counterattack on Germany. When they defeated Germany at the Battle of Stalingrad, they were forced to surrender by 31 January 1943. That same year, British and American troops defeated the Italian and German forces in North Africa. Thus, Mussolini's government collapsed in July.
The Allied Powers celebrated "D-Day" on June 6, 1944, when they invaded the German-controlled part of France on Normandy Beach by installing troops from the United States, Canada and Britain, forcing Hitler to concentrate most of his army's power on the Western Front. He fought in the Battle of the Bulge, between December 1944 and January 1945, and eventually lost on the Eastern Front to the Soviets, advancing to the borders of Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Romania to capture.

On April 30, Hitler committed suicide and on May 8, Germany surrendered to the Soviets, who had then conquered most of mainland Germany. At the Postdam Conference held in July-August 1945, American, British and Soviet leaders discussed dividing German land to rule. They also came up with plans to meet Japan.
From the aftermath of the Battle of Iwo Jima and the Battle of Okinawa, the United States feared a dangerous and costly invasion of Japan. Therefore, it succumbed to the use of destructive and deadly nuclear weapons. It bombed the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in early August. Consequently, Japan accepted the terms of Postdam on September 2 and formally surrendered to the Soviet Union, marking the end of World War II.


